Mouse IL-17A ELISA Kit (96-well)
USD 415.00
3 Weeks*
Product Images

Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 96-well strip plate |
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Assay Length | 3 hour |
| Signal | Colorimetric |
| Curve Range | 7.8 - 500 pg/mL |
| Sample Type | Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin) |
| Sample Volume | 20 uL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant Mouse IL-17A Ligand |
| Sensitivity | 4pg/mL |
| Reactivities | Mouse |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules. |
| Components |
|
| Background | Mouse Interleukin 17 (IL-17; also known as IL-17A and CTLA-8) is a 21 kDa, variably glycosylated polypeptide that belongs to the IL-17 family of cytokines containing a cysteine-knot fold . Its sequence was originally isolated from an activated hybridoma created from the fusion of a mouse cytotoxic and rat T cell lymphoma cell line . It is synthesized as a 158 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 25 aa signal sequence and a 15 kDa, 133 aa mature segment . In both mouse and human, there is one conserved N-linked glycosylation site that likely contributes 5 kDa to its native molecular weight. IL-17A forms both a 35-38 kDa homodimer,and a 45-48 kDa heterodimer with IL-17F . Mature mouse IL-17A is 61% and 89% aa identical to human and rat IL-17A, respectively . While rodent and human mature sequences show modest aa sequence identity, human IL-17 is active on both mouse and rat cells . Cells known to produce IL-17 are the CD4+ Th17 T cells, Paneth cells, GR1+CD11b+ myeloid suppressor cells, CD27-.. T cells, CD1+NK1.1- iNKT cells and CD3-CD4+ LTi-like cells(3, 5, 6, 10-12). A high affinity receptor for mouse IL-17 has been reported, and appears to be a heteromultimer of IL-17RA and IL-17RC, likely in a 2:1 ratio . IL-17RA is a 130 kDa, type I transmembrane glycoprotein that bears no resemblance to members of the cytokine, TNF or immunoglobulin receptor superfamily . IL-17RC is also a type I transmembrane protein, approximately 90-95 kDa in size, that shares less than 30% aa identity with IL-17RA . Both receptors are needed for IL-17A and IL-17A/F activity. The two receptors appear to form a functional association following ligand binding to IL-17RA . IL-17 is best known for its participation in the recruitment and survival of neutrophils . Its induction was initially described to be the result of antigen stimulation of dentritic cells, resulting in IL-23 secretion. In a TCR-independent event, IL-23 induces T cell production of IL-17. Once secreted, IL-17 in the bone marrow would seem to induce stromal/fibroblast expression of both G-CSF and SCF (membrane form), an effect that increases neutrophil differentiation and activation. IL-17 may complement this by directly blocking neutrophil apoptosis, promoting greater circulating neutrophil numbers . In the tissues, IL-17 seems to promote neutrophil extravasation, principally through its effects on macrophages and endothelial cells (EC). On macrophages, IL-17 induces TNF-., IL-1. and IL-6 production .TNF-. and IL-1. then act on local ECs to induce G-CSF secretion, an effect that is potentiated by IL-17 . IL-17 further contributes to neutrophil influx by inducing EC CXC chemokine release and NO production, which may increase vascular permeability . IL-17 effects are not limited to neutrophils. In synovial joints, IL-17 upregulates RANKL expression on osteoblasts. This provides a stimulus for osteoclast formation and subsequent bone resorption . |
| Gene Symbol | Il17a |
| Standard Curve |
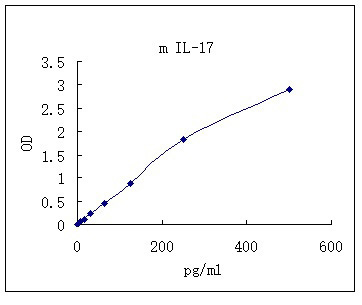
Representative standard curve for IL-17 ELISA. IL-17 was diluted in serial two-fold steps in Sample Diluent.
|
Documents
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China