Liver Diseases
Liver diseases can be acquired and inherited. In either case, the stages through which a liver disease progresses is quite similar which includes inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis and end-state liver disease. If detected in the earlier stages, the prognosis is good but in later stages starting from cirrhosis, it can be life threatening. The key is to detect and treat liver diseases early.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): It is a buildup of excessive fat in the liver that can lead to liver damage resembling the damage caused by alcohol abuse, but that occurs in people who do not drink heavily. There is a general consensus that NAFLD contributes to a number of liver cirrhosis cases and individuals with NAFLD have increased risk for hepatocellular cancer. NAFLD and cirrhosis together forms a group of condition called metabolic syndrome.
HSD17B13* MIR10B* MIR122* MIR140 MIR21 MIR22 MIR34A MSR1 PNPLA3
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): NASH, a silent liver disease, is characterized by accumulation of fat in liver along with inflammation and structural damage. Presence of fibrosis is variable. Key pathways involved in NASH include the respiratory electron transport, ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis coupling, and common cytokine receptor gamma chain family of signaling pathways.
HSD17B13* GGT1 GPT IL6 INS* PON1 PPARA PPARG PTEN SLC17A5 TNF
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): HCC, a cancer of liver, is one of the human neoplasms associated with viral factors. Studies have shown that genetic and epigenetic changes occur after exposure to alcohol or aflatoxin B1 or HBV/HCV infection. Key pathways involved in HCC include chromatic remodeling, oxidative stress pathways, cell cycle regulation, Wnt/bet-catenin pathway, PIK-AK pathway, and telomere maintenance pathways.
APC ARID1A ARID2 AXIN1 CASP8 CTNNB1 IGF2R MET MIR23B MIR34A PDGFRL PIK3CA TERT TP53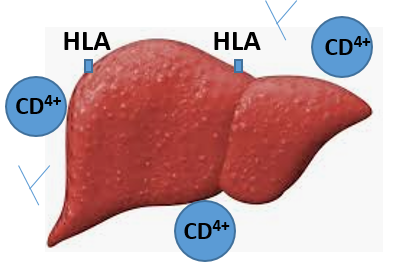
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH): AIH, a chronic liver inflammation disorder with unclear etiology, may be a result of an altered immune system, a genetic predisposition or environmental conditions. The defective immune system induces t-cell mediated attack on liver antigens, leading to necro-inflammation and liver damage.
AIRE CTLA4 CYP2D6 DLAT F2 FTCD GGT1 GOLM1 GPT SEPSECS
References
'*' indicates key genes
References
- An HSD17B13 variant reduces cirrhosis risk, Thomas H, Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 15, 328, 2018.
- Genetic susceptibility to autoimmune liver disease, Jochen Mattner, World J Hepatol., 3 (1), 1-7, 2011.
- New Insights in Genetic Cholestasis: From Molecular Mechanism to Clinical Implications, Sticova et al., Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,, 2018, Article ID 2313675.
- Noninvasive biomarkers in NAFLD and NASH ? current progress and future promise, Wong et al., Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 15, 461-478, 2018.
- Harnessing big ?omics?data and AI for drug discovery in HCC, Chen et al., Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 17, 238-251, 2020
- Liver Cirrhosis, Nature reviews gastroenterology and hepatology, 2019.
- HCV-Associated Liver Fibrosis and HSD17B13, About et. al, NEJM, Nov 8, 2018.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China