Huntington's Disease
Huntington?s disease (HD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder which usually occurs in mid-age. It is characterized by psychiatric disorders, involuntary movements and dementia, leading to death within 10-20 years
Huntingtin is a 350 kDa protein that is altered in HD. The expanded trinucleotide CAG repeat of the huntingtin gene encodes an abnormally expanded polyglutamine stretch in the N-terminus of the protein. The abnormal form of huntingtin aggregates in vitro and forms neuronal intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions in HD patients. Furthermore, the expanded polyglutamine repeats have been proposed to cause neuronal degeneration in HD through abnormal interactions with other proteins containing short polyglutamine tracts such as the CREB binding protein (CBP). CREB promotes cell survival and is a major mediator of survival signals in mature neurons.
Huntingtin-interacting proteins
HIP1 (Huntingtin-interacting protein 1) was identified as a protein that associates with huntingtin. Binding of HIP1 to huntingtin is dramatically reduced following polyglutamine expansion, strongly implicating this interaction in the disease process. Huntingtin has also been shown to interact with the following proteins: GAPDH, HAP1, HIP7 (Huntingtin-interacting protein 7, Optineurin) and HIP2 (Huntingtin-interacting protein 2). HIP2 is a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme which binds selectively to a large region at the N-terminus of huntingtin. HIP2-driven ubiquitination of huntingtin marks it for selective degradation via the proteasomal pathway. HIP2 may mediate foam cell formation by the suppression of apoptosis.
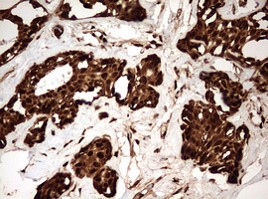
GAPDH IHC staining with anti-GAPDH mouse monoclonal antibody, cat# TA802563, of paraffin-embedded Human breast tissue within the normal limits (Heat-induced epitope retrieval by 10mM citric buffer, pH6.0, 120C for 3min).
HIP9 (Huntingtin-interacting protein 9 ) is the alpha subunit of the adaptor protein complex 2 (AP-2) which participates in membrane traffic pathways. AP-2 plays a key role in clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Cargo proteins are ferried into clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) which fuse with the early endosome. HIP9 (AP-2 alpha subunit) is responsible for orienting AP-2 on the membrane (binding accessible polyphosphoinositi-decontaining lipids) and also recognizing and binding to endocytosis signal motif [ED]-X-X-X-L-[LI] of endocytic transmembrane accessory proteins via its C-terminal cytosolic tail.
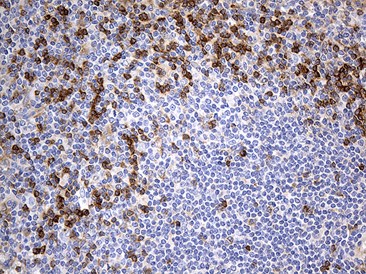
IHC staining with anti-optineurin mouse monoclonal antibody, cat# TA812132, of paraffin-embedded Human spleen tissue within the normal (Heat-induced epitope retrieval by 1mM EDTA in 10mM Tris buffer (pH8.5) at 120?C for 3 min).
HIP14 is a novel huntingtin-interacting protein. Its interaction with huntingtin is inversely correlated to the polyglutamine length of huntingtin. HIP14 protein, which is enriched in the brain, has been reported to show partial co-localization with huntingtin in the striatum. It is found in a subset of neurons affected in HD. One related protein is HIP14-like (HIP14L), which has 69 % homology to HIP14.
Huntingtin-associated protein-1 (HAP1) is highly expressed in brain and has been demonstrated to mediate the neuropathology of HD. HAP1 interacts with huntingtin, with two cytoskeletal proteins (dynactin and pericentriolar autoantigen protein 1) and with a hepatocyte growth factorregulated tyrosine kinase substrate. The interactions with cytoskeletal proteins and a kinase substrate indicate a role for HAP1 in vesicular trafficking or organelle transport.
| Gene/Protein | Description | SKU |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | anti hu GAPDH mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA802563 |
| GAPDH | anti hu GAPDH mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA802524 |
| GAPDH | hu GAPDH CRISPR kit | KN402309 |
| GAPDH | hu GAPDH shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL312841V |
| Huntingtin | Huntingtin (HTT) Human Recombinant Protein | TP318435 |
| Huntingtin | anti hu, ms Huntington mouse monocl. antibody; for WB | TA309937 |
| Huntingtin | Huntingtin (HTT) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: HDB4E10] | SM1661 |
| Huntingtin | hu Huntingtin CRISPR kit | KN418435 |
| Huntingtin | hu Huntingtin shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL312497V |
| HIP1 | anti hu HIP1 mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA804377 |
| HIP1 | anti hu HIP1 mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, ICH | TA804083 |
| HIP1 | hu HIP1 CRISPR kit | KN411418 |
| HIP1 | hu HIP1 shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL312457V |
| HIP2 | HIP2 (UBE2K) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | TA324679 |
| HIP2 | hu HIP2 CRISPR kit | KN408645 |
| HIP2 | hu HIP2 shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL312455V |
| HIP7/Optineurin | Anti hu Optineurin mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA812132 |
| HIP7/Optineurin | Anti hu, ms, rt Optineurin rabbit polycl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA332444 |
| HIP7/Optineurin | hu Optineurin CRISPR kit | KN402470 |
| HIP7/Optineurin | hu Optineurin shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL311010V |
| HIP9 | hu HIP9 rabbit polycl. antibody; for WB, IHC, FC | TA325045 |
| HIP9 | hu, ms, rt HIP9 rabbit polycl. antibody; for WB | TA332663 |
| HIP9 | hu HIP9 CRISPR kit | KN403018 |
| HIP9 | hu HIP9 shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL314753V |
| HIP14 | Anti hu, ms HIP14 goat polycl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA302507 |
| HIP14 | hu, bov, ms, rt, dog, pig, horse, rb HIP14 rabbit polycl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA341967 |
| HIP14 | hu HIP14 CRISPR kit | KN407982 |
| HIP14 | hu HIP14 shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL300348V |
| HAP1 | anti hu, ms, rt HAP1 mouse monocl. antibody; for WB, IHC | TA309681 |
| HAP1 | Anti hu, ms, rt HAP1 rabbit polycl. antibody; for WB, IHC, IF | TA306425 |
| HAP1 | hu HAP1 CRISPR kit | KN420251 |
| HAP1 | hu HAP1 shRNA as lentiviral particles | TL304153V |






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China