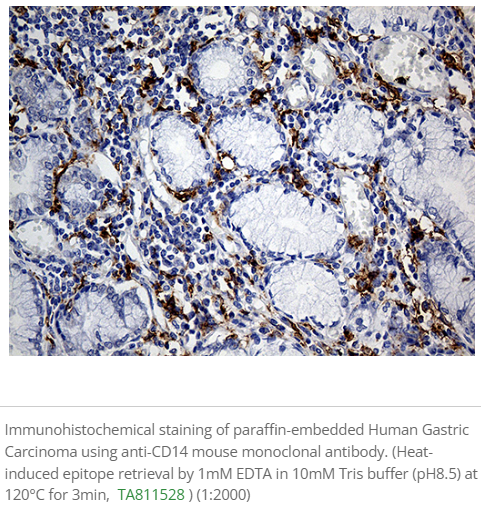
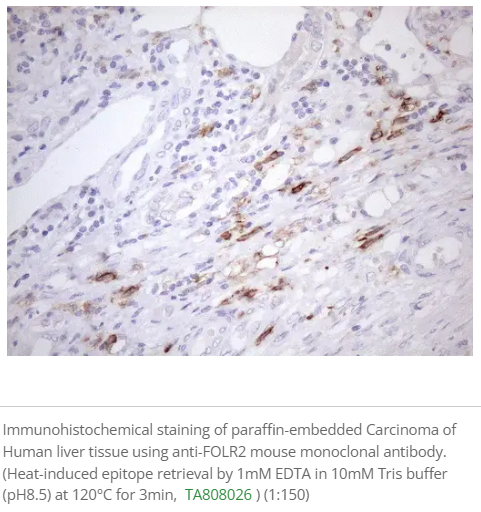
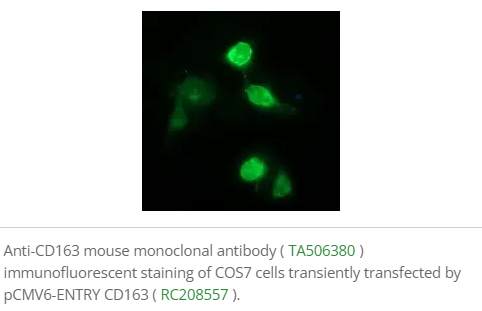
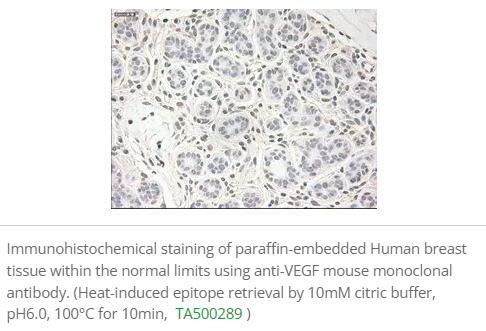
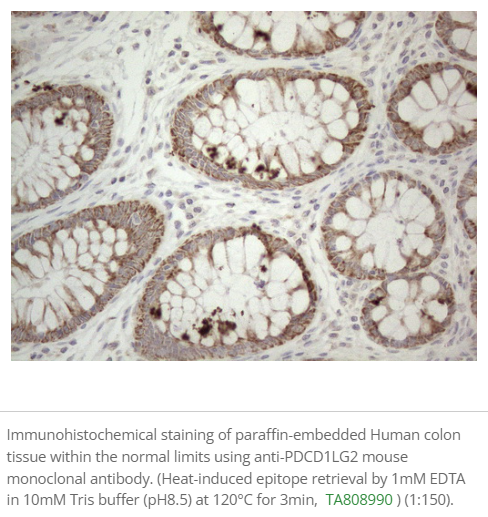
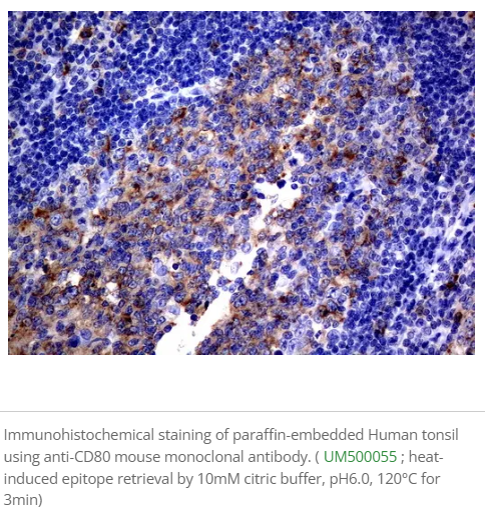
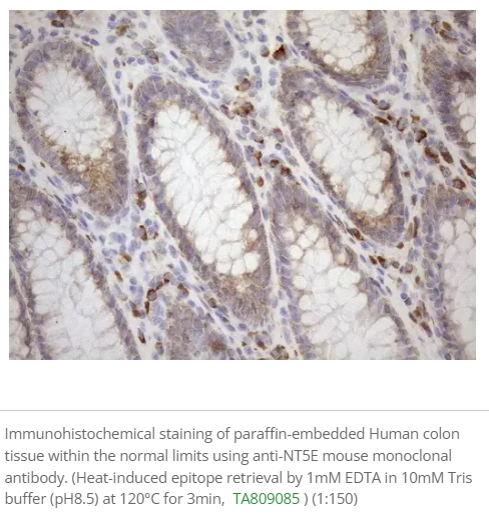
Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Tumor-Associated Macrophages Antibody Panel
Order the entire panel or check the box and add it to the cart to create a custom panel.
Tumor Microenvironment(TME) and TAMs
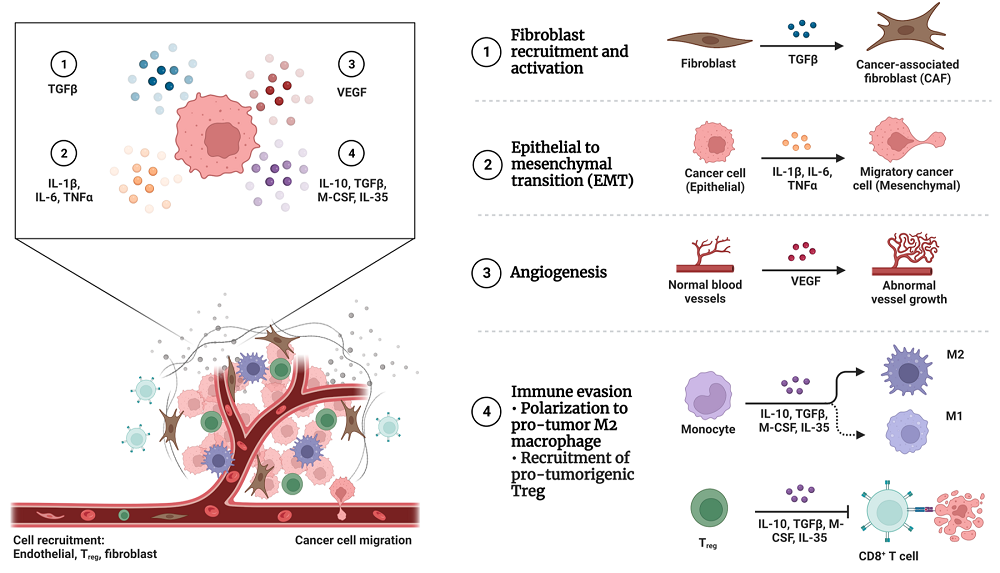
Key biomarkers in TME being used for Tumor Immunotherapy
PD-1 PD-L1 CTLA4 TIM3 LAG-3 NR2F6 TIGIT VISTA BTLATypes of TAM
Macrophages in the tumor microenvironment can be polarized into two functional states: M1 & M2 state. The M1 polarized macrophages, also known as the classically activated macrophages, respond to bacterial agents or IFN-Y. They produce proinflammatory and immunostimulatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-23. Studies have shown that M1 macrophages have anti-tumoral properties; they scavenge and destroy phagocytosed tumor cells.
On the other hand, M2-polarized macrophages, also known as alternatively activated macrophages, have the function of tissue reconstruction, debris removal, and promoting angiogenesis. IL-4 and IL-13, and other factors activate M2 macrophages. Most tumor-associated macrophages resemble M2 macrophages, and some as M1. M1 & M2 macrophages are two faces of the same coin; their expression depends on the level of cytokines in the environment. This spectrum of M1 & M2 macrophages also changes during tumor development. Thus, understanding TAMs will help develop more effective immunotherapies.
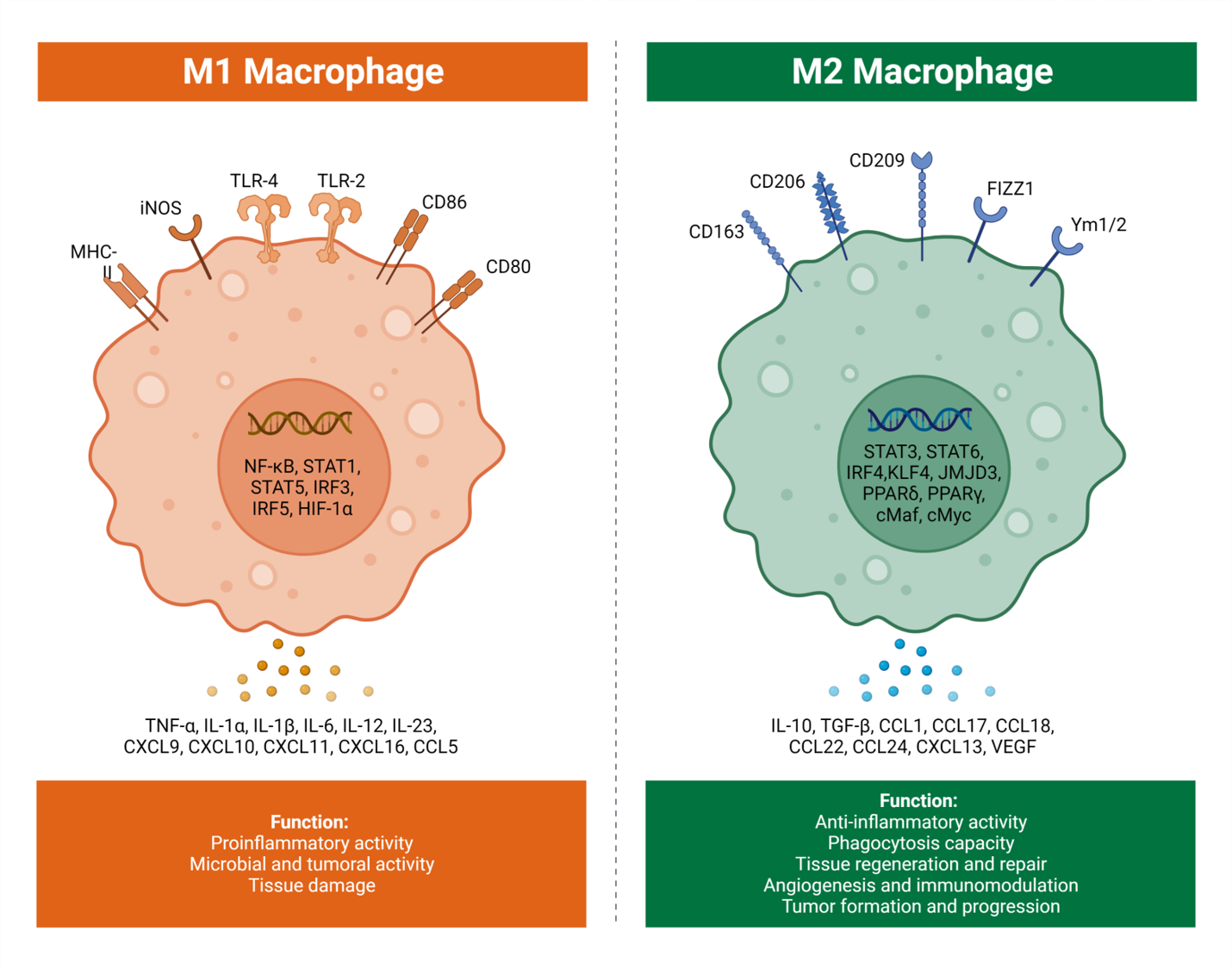
Key macrophage biomarkers in tumor microenvironment
CD47 IDO Adenosine IL-41 TGF-B TLR STING CD40 CD39
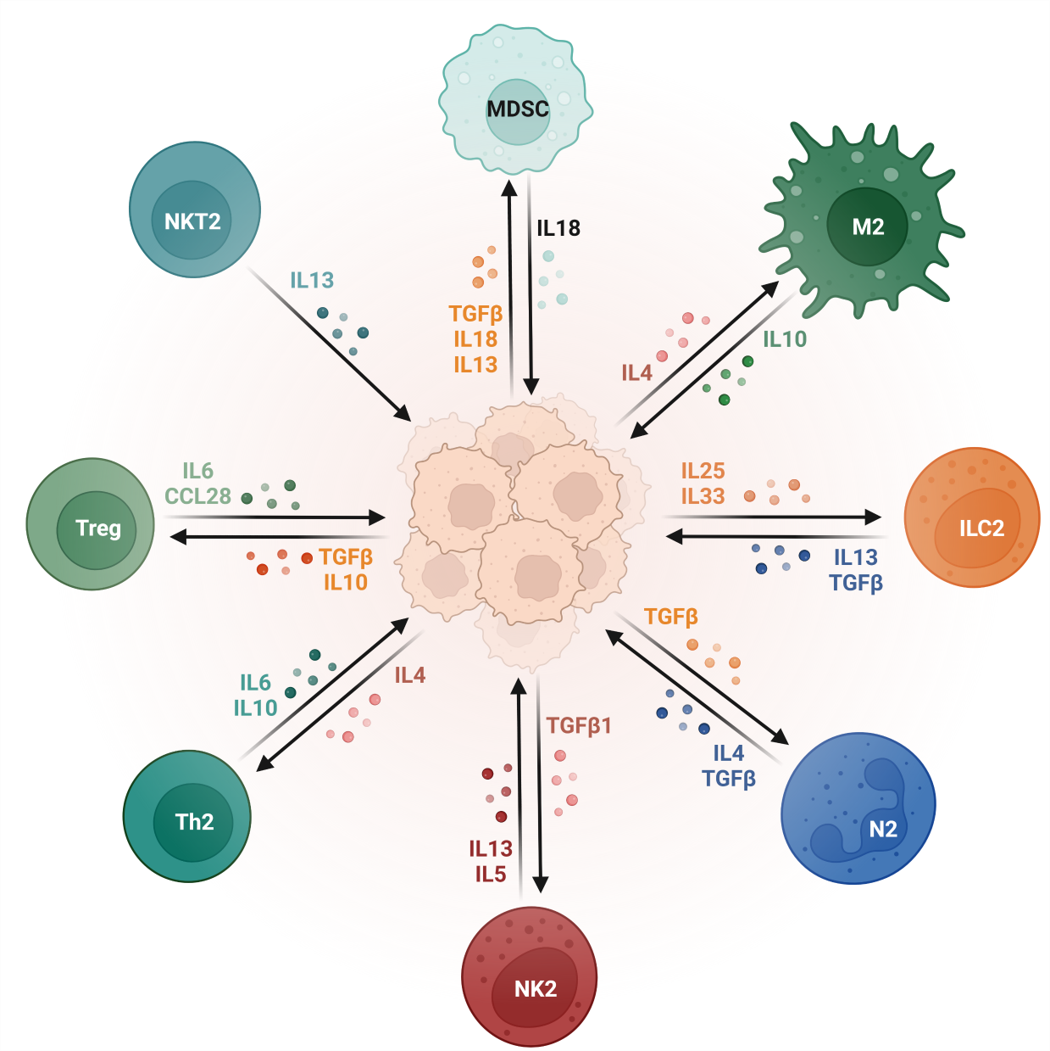
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) mediated immunosuppression
TAMs are a heterogeneous population of cells that display a range of phenotypes depending on the type of tumor and their microenvironment. TAMs use multiple mechanisms to inhibit anti-tumor immune response :
a) Production of inhibitory cytokines and chemokines: TAMs can secrete chemokines and cytokines that promote tumor development, such as IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10.
b) Amino-acid depletion - inhibits CD4 and CD8+ T cells by regulating L-tryptophan degradation in the Kynurenine pathway.
c) Inhibition of tumor cell phagocytosis- It regulates SIRP?/CD47 pathway to protect tumor cells from phagocytosis.
d) Production of PGE2 and Tregs-recruiting chemokine: It inhibits IFN-gamma production through regulating PGE2 production and upregulated Th17 response to inhibit T-cell response indirectly.
e) Direct engagement of T cell inhibitory receptor.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China