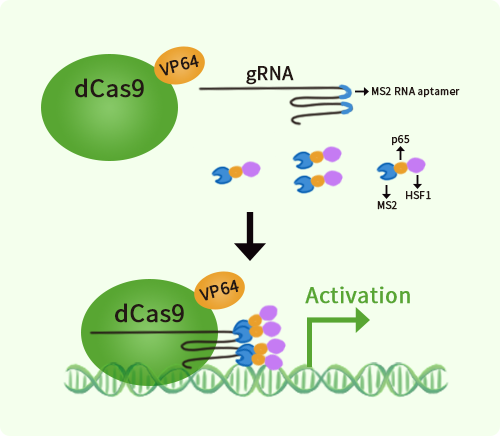
Human KCNA5 activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA102517
KCNA5 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 5
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3gRNAs, 1 scramble ctrl and 1 enhancer vector |
| Symbol | KCNA5 |
| Locus ID | 3741 |
| Kit Components | GA102517G1, KCNA5 gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA102517G2, KCNA5 gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA102517G3, KCNA5 gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_002234 |
| Synonyms | ATFB7; HCK1; HK2; HPCN1; KV1.5; PCN1 |
| Summary | 'Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ino channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. Four sequence-related potassium channel genes - shaker, shaw, shab, and shal - have been identified in Drosophila, and each has been shown to have human homolog(s). This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, shaker-related subfamily. This member contains six membrane-spanning domains with a shaker-type repeat in the fourth segment. It belongs to the delayed rectifier class, the function of which could restore the resting membrane potential of beta cells after depolarization and thereby contribute to the regulation of insulin secretion. This gene is intronless, and the gene is clustered with genes KCNA1 and KCNA6 on chromosome 12. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial atrial fibrillation type 7 (ATFB7). [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN419793 | KCNA5 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China