Shugoshin (SGO1) Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN404753
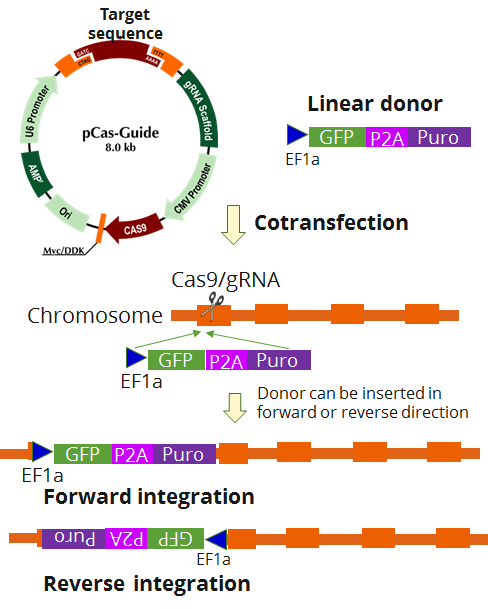
SGOL1 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN404753 is the updated version of KN204753.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "SGO1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | SGO1 |
| Locus ID | 151648 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001012409, NM_001012410, NM_001012411, NM_001012412, NM_001012413, NM_001199251, NM_001199252, NM_001199253, NM_001199254, NM_001199255, NM_001199256, NM_001199257, NM_138484, NR_131179, NR_131180 |
| Synonyms | CAID; NY-BR-85; SGO; SGOL1 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the shugoshin family of proteins. This protein is thought to protect centromeric cohesin from cleavage during mitotic prophase by preventing phosphorylation of a cohesin subunit. Reduced expression of this gene leads to the premature loss of centromeric cohesion, mis-segregation of sister chromatids, and mitotic arrest. Evidence suggests that this protein also protects a small subset of cohesin found along the length of the chromosome arms during mitotic prophase. An isoform lacking exon 6 has been shown to play a role in the cohesion of centrioles (PMID: 16582621 and PMID:18331714). Mutations in this gene have been associated with Chronic Atrial and Intestinal Dysrhythmia (CAID) syndrome, characterized by the co-occurrence of Sick Sinus Syndrome (SSS) and Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) within the first four decades of life (PMID:25282101). Fibroblast cells from CAID patients exhibited both increased cell proliferation and higher rates of senescence. Pseudogenes of this gene have been found on chromosomes 1 and 7. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA115802 | SGO1 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human shugoshin 1 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China