MAP3K4 Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN417201
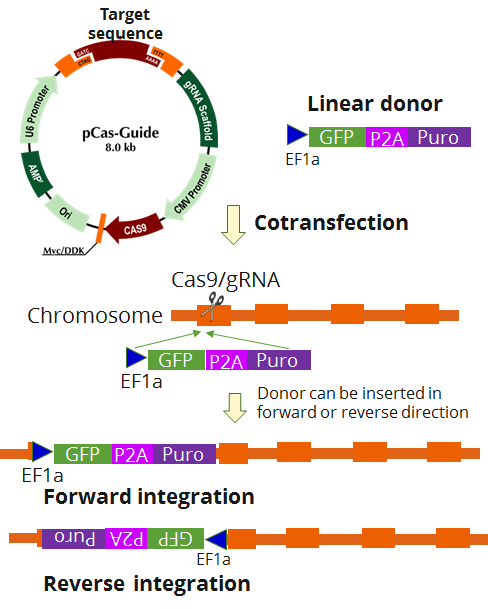
MAP3K4 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN417201 is the updated version of KN217201.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "MAP3K4"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | MAP3K4 |
| Locus ID | 4216 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001291958, NM_001301072, NM_005922, NM_006724, NR_120425, NM_001363582 |
| Synonyms | MAPKKK4; MEKK 4; MEKK4; MTK1; PRO0412 |
| Summary | 'The central core of each mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a conserved cascade of 3 protein kinases: an activated MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK) phosphorylates and activates a specific MAPK kinase (MAPKK), which then activates a specific MAPK. While the ERK MAPKs are activated by mitogenic stimulation, the CSBP2 and JNK MAPKs are activated by environmental stresses such as osmotic shock, UV irradiation, wound stress, and inflammatory factors. This gene encodes a MAPKKK, the MEKK4 protein, also called MTK1. This protein contains a protein kinase catalytic domain at the C terminus. The N-terminal nonkinase domain may contain a regulatory domain. Expression of MEKK4 in mammalian cells activated the CSBP2 and JNK MAPK pathways, but not the ERK pathway. In vitro kinase studies indicated that recombinant MEKK4 can specifically phosphorylate and activate PRKMK6 and SERK1, MAPKKs that activate CSBP2 and JNK, respectively but cannot phosphorylate PRKMK1, an MAPKK that activates ERKs. MEKK4 is a major mediator of environmental stresses that activate the CSBP2 MAPK pathway, and a minor mediator of the JNK pathway. Several alternatively spliced transcripts encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA102873 | MAP3K4 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China