TAF4 Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN423691
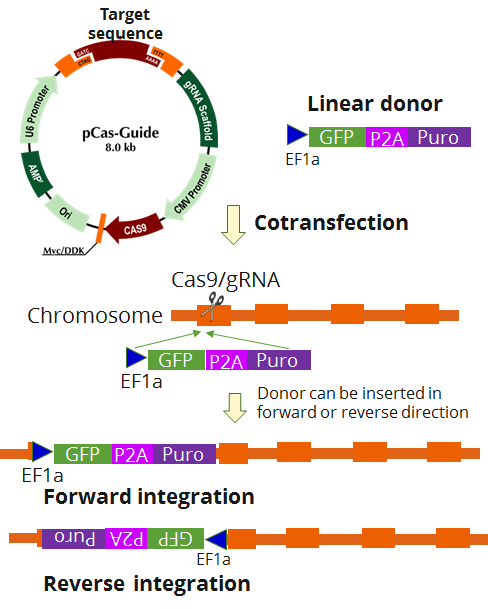
TAF4 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN423691 is the updated version of KN223691.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "TAF4"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | TAF4 |
| Locus ID | 6874 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_003185 |
| Synonyms | TAF2C; TAF2C1; TAF4A; TAFII130; TAFII135 |
| Summary | 'Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II requires the activities of more than 70 polypeptides. The protein that coordinates these activities is transcription factor IID (TFIID), which binds to the core promoter to position the polymerase properly, serves as the scaffold for assembly of the remainder of the transcription complex, and acts as a channel for regulatory signals. TFIID is composed of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and a group of evolutionarily conserved proteins known as TBP-associated factors or TAFs. TAFs may participate in basal transcription, serve as coactivators, function in promoter recognition or modify general transcription factors (GTFs) to facilitate complex assembly and transcription initiation. This gene encodes one of the larger subunits of TFIID that has been shown to potentiate transcriptional activation by retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 receptors. In addition, this subunit interacts with the transcription factor CREB, which has a glutamine-rich activation domain, and binds to other proteins containing glutamine-rich regions. Aberrant binding to this subunit by proteins with expanded polyglutamine regions has been suggested as one of the pathogenetic mechanisms underlying a group of neurodegenerative disorders referred to as polyglutamine diseases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA104733 | TAF4 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human TATA-box binding protein associated factor 4 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China