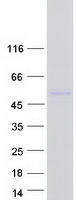
FADS2 (NM_004265) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH323780
FADS2 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_004256)
Other products for "FADS2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC223780 |
| Predicted MW | 52.1 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC223780 representing NM_004265
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MGKGGNQGEGAAEREVSVPTFSWEEIQKHNLRTDRWLVIDRKVYNITKWSIQHPGGQRVIGHYAGEDATD AFRAFHPDLEFVGKFLKPLLIGELAPEEPSQDHGKNSKITEDFRALRKTAEDMNLFKTNHVFFLLLLAHI IALESIAWFTVFYFGNGWIPTLITAFVLATSQAQAGWLQHDYGHLSVYRKPKWNHLVHKFVIGHLKGASA NWWNHRHFQHHAKPNIFHKDPDVNMLHVFVLGEWQPIEYGKKKLKYLPYNHQHEYFFLIGPPLLIPMYFQ YQIIMTMIVHKNWVDLAWAVSYYIRFFITYIPFYGILGALLFLNFIRFLESHWFVWVTQMNHIVMEIDQE AYRDWFSSQLTATCNVEQSFFNDWFSGHLNFQIEHHLFPTMPRHNLHKIAPLVKSLCAKHGIEYQEKPLL RALLDIIRSLKKSGKLWLDAYLHK TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | 50 ug/ml as determined by BCA |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 100 mM glycine, 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.3. Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_004256 |
| RefSeq Size | 3149 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1332 |
| Synonyms | D6D; DES6; FADSD6; LLCDL2; SLL0262; TU13 |
| Locus ID | 9415 |
| UniProt ID | O95864 |
| Cytogenetics | 11q12.2 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) gene family. Desaturase enzymes regulate unsaturation of fatty acids through the introduction of double bonds between defined carbons of the fatty acyl chain. FADS family members are considered fusion products composed of an N-terminal cytochrome b5-like domain and a C-terminal multiple membrane-spanning desaturase portion, both of which are characterized by conserved histidine motifs. This gene is clustered with family members at 11q12-q13.1; this cluster is thought to have arisen evolutionarily from gene duplication based on its similar exon/intron organization. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013] |
| Protein Families | Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism, Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, PPAR signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China