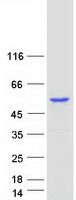
ABAT (NM_020686) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP318980
Recombinant protein of human 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 1
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC218980. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 53.2 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_065737 |
| Locus ID | 18 |
| UniProt ID | P80404, X5D8S1 |
| Cytogenetics | 16p13.2 |
| Refseq Size | 4814 |
| Refseq ORF | 1500 |
| Synonyms | GABA-AT; GABAT; NPD009 |
| Summary | '4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT) is responsible for catabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an important, mostly inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, into succinic semialdehyde. The active enzyme is a homodimer of 50-kD subunits complexed to pyridoxal-5-phosphate. The protein sequence is over 95% similar to the pig protein. GABA is estimated to be present in nearly one-third of human synapses. ABAT in liver and brain is controlled by 2 codominant alleles with a frequency in a Caucasian population of 0.56 and 0.44. The ABAT deficiency phenotype includes psychomotor retardation, hypotonia, hyperreflexia, lethargy, refractory seizures, and EEG abnormalities. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein isoform have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, beta-Alanine metabolism, Butanoate metabolism, Metabolic pathways, Propanoate metabolism, Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC400218 | ABAT HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC412383 | ABAT HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC426789 | ABAT HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY400218 | Transient overexpression lysate of 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 2 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY412383 | Transient overexpression lysate of 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 1 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY426789 | Transient overexpression lysate of 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), transcript variant 3 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| PH306793 | ABAT MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_000654) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| PH318980 | ABAT MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_065737) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| PH325860 | ABAT MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_001120920) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| TP306793 | Recombinant protein of human 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 2 |
USD 823.00 |
|
| TP325860 | Recombinant protein of human 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT), transcript variant 3 |
USD 748.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China