PRKACA (NM_207518) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP320877
Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha (PRKACA), transcript variant 2
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC220877. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 39.6 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
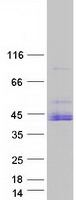
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_997401 |
| Locus ID | 5566 |
| UniProt ID | P17612, A8K8B9 |
| Cytogenetics | 19p13.12 |
| Refseq Size | 2490 |
| Refseq ORF | 1029 |
| Synonyms | PKACA; PPNAD4 |
| Summary | 'This gene encodes one of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A, which exists as a tetrameric holoenzyme with two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits, in its inactive form. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase A is important to many cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Constitutive activation of this gene caused either by somatic mutations, or genomic duplications of regions that include this gene, have been associated with hyperplasias and adenomas of the adrenal cortex and are linked to corticotropin-independent Cushing's syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Tissue-specific isoforms that differ at the N-terminus have been described, and these isoforms may differ in the post-translational modifications that occur at the N-terminus of some isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis, Calcium signaling pathway, Chemokine signaling pathway, Dilated cardiomyopathy, Gap junction, GnRH signaling pathway, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Insulin signaling pathway, Long-term potentiation, MAPK signaling pathway, Melanogenesis, Olfactory transduction, Oocyte meiosis, Prion diseases, Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation, Taste transduction, Vascular smooth muscle contraction, Vibrio cholerae infection, Wnt signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC403918 | PRKACA HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC419140 | PRKACA HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY403918 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha (PRKACA), transcript variant 2 |
USD 396.00 |
|
| LY419140 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha (PRKACA), transcript variant 1 |
USD 396.00 |
|
| PH310332 | PRKACA MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_002721) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| PH320877 | PRKACA MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_997401) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| TP310332 | Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha (PRKACA), transcript variant 1 |
USD 823.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China