COX4 (COX4I1) (NM_001861) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP761888
Purified recombinant protein of Human cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV isoform 1 (COX4I1), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, full length, with N-terminal GST and C-terminal His tag, expressed in E.coli, 50ug
Other products for "COX4I1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length COX4I1
|
| Tag | N-GST and C-His |
| Predicted MW | 35.2 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
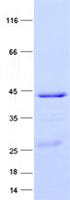
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25mM Tris, pH8.0,150mM NaCl,10% glycerol,1%Sarkosyl |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001852 |
| Locus ID | 1327 |
| UniProt ID | P13073 |
| Cytogenetics | 16q24.1 |
| Refseq Size | 839 |
| Refseq ORF | 507 |
| Synonyms | COX4; COX4-1; COXIV; COX IV-1; COXIV-1 |
| Summary | 'Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) is the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It is a multi-subunit enzyme complex that couples the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to molecular oxygen and contributes to a proton electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The complex consists of 13 mitochondrial- and nuclear-encoded subunits. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits perform the electron transfer and proton pumping activities. The functions of the nuclear-encoded subunits are unknown but they may play a role in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This gene encodes the nuclear-encoded subunit IV isoform 1 of the human mitochondrial respiratory chain enzyme. It is located at the 3' of the NOC4 (neighbor of COX4) gene in a head-to-head orientation, and shares a promoter with it. Pseudogenes related to this gene are located on chromosomes 13 and 14. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]' |
| Protein Families | Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Alzheimer's disease, Cardiac muscle contraction, Huntington's disease, Metabolic pathways, Oxidative phosphorylation, Parkinson's disease |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China