MAGI3 (GKWW domain) Sheep Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "MAGI3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
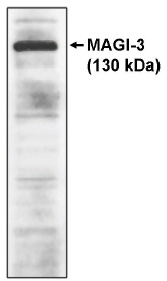
| Recommended Dilution | Western Blot: 1 - 10 µg/ml. Detects a 130 kDa band in cells transfected with full-length MAGI-3 protein. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Sheep |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein corresponding to the guanylate kinase-WW domain of MAGI-3. |
| Specificity | This antibody reacts to MAGI-3, GKWW. |
| Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline with 0.08% sodium azide State: Purified State: Liquid purified Ig (0.2 µm sterile filtered) |
| Concentration | Lot specific |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 3 (MAGI3), transcript variant 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Membrane-associated guanylate kinase with inverted orientation (MAGI3) is a novel, 130 kDa guanylate kinase which is part of a family of multi-PDZ domain containing guanylate kinases. These guanylate kinases are localized to epithelial cell tight junctions. MAGI3 and PTEN/MMAC cooperate to modulate the kinase activity of AKT/protein kinase B (PKB). MAGI3 positions the PTEN/MMAC phosphatase to specific subcellular locations that are involved with the regulation of cell proliferation and survival. MAGI3, as well as other proteins in this family, are made up of an N-terminal guanylate kinase domain, followed by a WW domain, named for two conserved tryptophan residues and first identified as two repeats in mouse YAP65, which is them followed by 5 PDZ domains. |
| Synonyms | MAGI-3 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Tight junction |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China