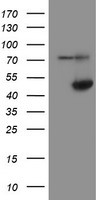
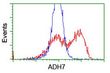
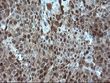
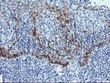
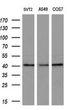
ADH7 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI2H10]
CAT#: CF504873
Carrier-free (BSA/glycerol-free) ADH7 mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI2H10 (formerly 2H10)
Formulation: Standard
Frequently bought together (2)
Other products for "ADH7"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | OTI2H10 |
| Applications | FC, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500~2000, IHC 1:150, FLOW 1:100 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Full length human recombinant protein of human ADH7(NP_000664) produced in HEK293T cell. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized powder (original buffer 1X PBS, pH 7.3, 8% trehalose) |
| Reconstitution Method | For reconstitution, we recommend adding 100uL distilled water to a final antibody concentration of about 1 mg/mL. To use this carrier-free antibody for conjugation experiment, we strongly recommend performing another round of desalting process. (OriGene recommends Zeba Spin Desalting Columns, 7KMWCO from Thermo Scientific) |
| Purification | Purified from mouse ascites fluids or tissue culture supernatant by affinity chromatography (protein A/G) |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 41.3 kDa |
| Gene Name | alcohol dehydrogenase 7 (class IV), mu or sigma polypeptide |
| Database Link | |
| Background | This gene encodes class IV alcohol dehydrogenase 7 mu or sigma subunit, which is a member of the alcohol dehydrogenase family. Members of this family metabolize a wide variety of substrates, including ethanol, retinol, other aliphatic alcohols, hydroxysteroids, and lipid peroxidation products. The enzyme encoded by this gene is inefficient in ethanol oxidation, but is the most active as a retinol dehydrogenase; thus it may participate in the synthesis of retinoic acid, a hormone important for cellular differentiation. The expression of this gene is much more abundant in stomach than liver, thus differing from the other known gene family members. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq] |
| Synonyms | ADH4 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450, Fatty acid metabolism, Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis, Metabolic pathways, Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, Retinol metabolism, Tyrosine metabolism |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
| Antibody Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China