p53R2 (RRM2B) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "RRM2B"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
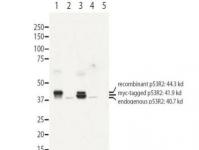
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:3,000, WB: 1 ug/mL, IHC: User Optimized, IF: User Optimized, IP: User Optimized |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Anti-Human RRM2B/p53R2 antibody was prepared by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to a region near the N-terminus of human RRM2B1 protein. A residue of cysteine was added to facilitate coupling. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | ribonucleotide reductase regulatory TP53 inducible subunit M2B |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | MTDPS8A; MTDPS8B; P53R2 |
| Note | RRM2B/p53-R2, or p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase small subunit 2-like protein, is a member of a broad superfamily of ferritin-like di-iron-carboxylate proteins. The RRM2B protein is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides that are essential for DNA synthesis, and is found in all eukaryotes. RRM2B plays a pivotal role in cell survival by repairing damaged DNA in a p53/TP53-dependent manner. It supplies deoxyribonucleotides for DNA repair in cells arrested at G1 or G2. It contains an iron-tyrosyl free radical center required for catalysis, and forms an active ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) complex with RRM1 which is expressed both in resting and proliferating cells in response to DNA damage. It is a heterotetramer with a large (RRM1) subunit, and interacts with p53/TP53. The interaction with RRM1 occurs in response to DNA damage and results in its translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus. It is widely expressed at a high level in skeletal muscle and at a weak level in thymus, and expressed in epithelial dysplasias and squamous cell carcinoma. Defects in RRM2B are the cause of encephalomyopathic mitochondrial depletion syndrome with renal tubulopathy (EMDSRT). Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MDS) is a clinically heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by a reduction in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number. The encephalomyopathic form with renal tubulopathy is presented with various combinations of hypotonia, tubulopathy, seizures, respiratory distress, diarrhea, and lactic acidosis. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Glutathione metabolism, Metabolic pathways, p53 signaling pathway, Purine metabolism, Pyrimidine metabolism |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China