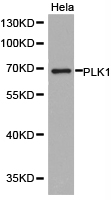
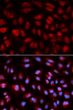
PLK1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
Recombinant protein of human polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) (PLK1)
USD 823.00
Transient overexpression lysate of polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) (PLK1)
USD 396.00
Other products for "PLK1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ICC/IF, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000;IHC 1:50- 1:200;IF 1:50- 1:200 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human PLK1 |
| Formulation | Store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | polo like kinase 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | At least four distinct polo-like kinases exist in mammalian cells: PLK1, PLK2, PLK3, and PLK4/SAK . PLK1 apparently plays many roles during mitosis, particularly in regulating mitotic entry and exit. The mitosis promoting factor (MPF), cdc2/cyclin B1, is activated by dephosphorylation of cdc2 (Thr14/Tyr15) by cdc25C. PLK1 phosphorylates cdc25C at Ser198 and cyclin B1 at Ser133 causing translocation of these proteins from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. PLK1 phosphorylation of Myt1 at Ser426 and Thr495 has been proposed to inactivate Myt1, one of the kinases known to phosphorylate cdc2 at Thr14/Tyr15. Polo-like kinases also phosphorylate the cohesin subunit SCC1, causing cohesin displacement from chromosome arms that allow for proper cohesin localization to centromeres. Mitotic exit requires activation of the anaphase promoting complex (APC), a ubiquitin ligase responsible for removal of cohesin at centromeres, and degradation of securin, cyclin A, cyclin B1, Aurora A, and cdc20. PLK1 phosphorylation of the APC subunits Apc1, cdc16, and cdc27 has been demonstrated in vitro and has been proposed as a mechanism by which mitotic exit is regulated.Substitution of Thr210 with Asp has been reported to elevate PLK1 kinase activity and delay/arrest cells in mitosis, while a Ser137Asp substitution leads to S-phase arrest. In addition, while DNA damage has been found to inhibit PLK1 kinase activity, the Thr210Asp mutant is resistant to this inhibition. PLK1 has been reported to be phosphorylated in vivo at Ser137 and Thr210 in mitosis; DNA damage prevents phosphorylation at these sites. |
| Synonyms | PLK; STPK13 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Cell cycle, Oocyte meiosis, Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China