Chrna1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
CAT#: TA328881
Rabbit Polyclonal Anti-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor alpha1 (extracellular)
Other products for "Chrna1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
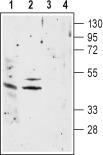
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide EHETRLVAKLFKD(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 22-34 of rat nAChRa1. Extracellular, N-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 1 subunit |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Acetylcholine, released by cholinergic neurons, activates two groups of acetylcholine receptors (AChRs); muscarinic AChRs (mAChRs) which belong to the superfamily of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and nicotinic AChRs (nAChRs) which belong to the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. nAChRs also respond to nicotine, hence their name.To date, 17 different but related subunits of nAChRs have been identified and cloned. They consist of a subunits (a1-10), which is responsible for the binding of ligands. In fact, this subunit includes a Cys-loop in the first extracellular domain that is required for agonist binding. The other subunits responsible for making up the active receptor are the Ã? (Ã?1-4), ?, d and e subunits. Structurally, all subunits have the following: a conserved large extracellular N-terminal domain, conserved transmembrane domains, a variable cytoplasmic loop and a fourth transmembrane domain with a short extracellular C-terminal domain. An active nAChR is generally a heteropentamer (homopentamers also exist) of these various subunits organized around a central pore.All a subunits are expressed in neuronal cells except for the a1 subunit which is specifically expressed in skeletal muscle. Indeed, two different nAChR structural entities with the following stoichiometry are observed in this tissue: (a1)2Ã?1d? in fetal muscle cells and (a1)2Ã?1de at mature neuromuscular synapses.The a1 extracellular domain contains the main immunogenic region, a region against which a large fraction of autoantibodies against nAChR is directed in the autoimmune disease myasthenia gravis (MG). This autoimmune disease is characterized by the malfunction of neuromuscular transmission as a result of nonfunctional nAChRs, leading to defective signaling at the neuromuscular junction.Due to its central role in muscle contraction and autonomic nervous system, nAChRs have evolved to be important targets of toxins secreted by plants, insects and animals. One prominent toxin affecting a1, in addition to other subunits, is a-bungarotoxin, a snake toxin which blocks nAChRs. |
| Synonyms | ACHRA; ACHRD; CHNRA; CHRNA; CMS2A; FCCMS; SCCMS |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China