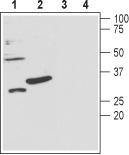
Kcnmb3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Kcnmb3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)HYDEEAIRTNPK, corresponding to amino acid residues 134- 145 of rat SloÃ?3. Extracellular loop. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M regulatory beta subunit 3 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Large-conductance, voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels, also known as the BK channels, are widely expressed channels that couple changes in submembrane Ca2+ concentration to the regulation of electrical excitability1. BK channels are formed from four a-subunits arising from the Slowpoke (Slo) gene product2. In addition, in smooth muscle and cochlea, an accessory Ã?-subunit can regulate BK channel gating profoundly. At present, four Ã? subunits have been cloned in mammals. Ã? Subunits alter the Ca2+ sensitivity and gating kinetics of BK channels, greatly contributing to BK channel diversity. On the other hand, they modify the BK channel pharmacological properties, changing toxin binding and acting as receptors for drugs.Regulatory Ã? subunits share a putative membrane topology, with two transmembrane segments connected by a 120- residue extracellular loop and with NH2 and COOH terminals oriented toward the cytoplasm4. Each Ã? subunit has a tissue-specific expression and modulates channel function uniquely which provides a major mechanism for diverse BK channel phenotypes in various tissues.Ã?3 is highly expressed in kidney, heart, and brain5. The Ã?3 gene (KCNMB3) associates with Slo1 a subunits and regulate BK channel function. In humans, the Ã?3 gene contains four N-terminal alternative exons that produce four functionally distinct Ã?3 subunits, Ã?3a-d. Three variants, Ã?3a-c, exhibit kinetically distinct inactivation behaviors6. A mutation in the Ã?3 gene is linked to idiopathic epilepsy7.kinetically distinct inactivation behaviors. A mutation in the β3 gene is linked to idiopathic epilepsy. |
| Synonyms | BKBETA3; HBETA3; K(VCA)beta-3; KCNMB2; KCNMBL; Slo-beta-3; SLOBETA3 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China