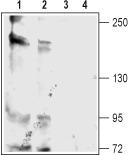
Kcnt2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Kcnt2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)KDVKDPGHHRSIHCCR, corresponding to amino acid residues 991-1004 of rat KCa4.2 . Intracellular, C-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium sodium-activated channel subfamily T member 2 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | KCa4.1 (Slack, Na+ activated K+ channel, Slo2.2, KCNT1) was originally cloned and named so due to its high similarity to the Slo genes1. Shortly after its discovery, KCa4.2 (Slick, Slo2.1, KCNT2), its sister channel was also cloned2. Although KCa4.2 (like KCa4.1) is functionally a Na+-activated K+ channel (KNa), it is termed KCa by the IUPHAR nomenclature, due to its sequence homology to other KCa channels. Both channels are activated by high intracellular concentrations of Na+. Like Slack, Slick contains six transmembrane spanning domains, a P-region between transmembrane regions 5 and 6 and intracellular N- and C-termini. However, the N-terminal domain of Slick is significantly shorter than that of Slack. In addition, contrary to Slack, Slick is regulated by ATP as it has an ATP binding site in its C-terminal domain2. ATP binding reduces the activity of the channel and mutations of this site abolish the inhibitory effect2. Both channels are regulated by intracellular Cl- ions, but Slick displays higher sensitivity3. Also, the overall electrical characteristics of Slick channels are different from those of Slack; Slick is rapidly activated in response to depolarization, and also has a basal level of activity in the absence of Na+. Both channels are highly expressed in the brain with overlapping expression. Slick is found in the midbrain, brainstem, and hippocampus and throughout the neocortex. This KNa channel is also detected in the auditory neurons in the brainstem. Detection of Slick was also found in the heart, although at much lower levels. Many different functions have been attributed to KNa channels including action potential repolarization, slow after-hyperpolarization, burst firing and adaptation after repetitive firing3. These channels also contribute to the response of neurons to hypoxia. |
| Synonyms | KCa4.2; MGC119610; MGC119611; MGC119612; MGC119613; SLICK; SLO2.1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China