Human Resistin ELISA Kit (96-well)
USD 415.00
3 Weeks*
Product Images

Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 96-well strip plate |
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Signal | Colorimetric |
| Curve Range | 7.8-500pg/ml |
| Sample Type | Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin) |
| Sample Volume | 20 uL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant Human Resistin Ligand |
| Sensitivity | 4pg/mL |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules. |
| Components |
|
| Background | Resistin, also known as Found In Inflammatory Zone 3 (FIZZ3) or Adipocyte Secreted Factor(ADSF), is a member of a protein family known as the Resistin-like molecules (RELMs). It is perhaps best known for its potential as a link between obesity and the development of insulin resistance . Other members of this family include RELM-./FIZZ1 and RELM-., which are described in rodents but as yet have no identified human counterparts, and RELM-./FIZZ2. The Resistin amino acid (aa) sequence contains a putative N-terminal signal sequence and a motif containing 11 cysteine residues, 10 of which are characteristic of the RELM family. The protein is thought to be secreted as a dimer and potentially exists in higher order molecular structures resulting from interactions between Resistin dimers or other members of the RELM family . A splice variant in the rat, lacking the signal sequence and localized predominantly to the nucleus, has also been described . A large 3' intron is the primary reason that the mouse genomic sequence is 3-fold larger than the corresponding human sequence . Mouse and human Resistin share only 53 percent identity at the aa level and exhibit differences in expression patterns . In mouse, expression appears primarily inadipose tissues . Although some human studies suggest Resistin is expressed by adipose tissues as well, the most significant source appears to be blood mononuclear cells . In humans, Resistin is also reported to be expressed by pre-adipocytes , placenta , pancreatic islets , and primary leukemia cells . A receptor for Resistin has not yet been described. Resistin acquired initial attention as a potential link between obesity and glucose regulation. Serum levels were shown to increase in diet-induced and genetic forms of obesity in mice (ob/ob and db/db) and decrease in response to insulin sensitizing drugs (TZDs) . In addition, function-blocking Resistin antibodies enhanced insulin actions while treatment with recombinant Resistin caused glucose intolerance and insulin resistance . Resistin knockout mice exhibit decreased fasting blood glucose levels as a result of reduced hepatic output . To establish a physiological role in humans, several studies have examined whether altered circulating Resistin levels are associated with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and/or obesity. Although some demonstrate significant correlations , others report no correlation , suggesting that in humans fundamental questions remain regarding ResistinÂ?s role in these pathophysiological processes . Resistin expression by human mononuclear cells could indicate a potential role in inflammation. In vitro, Resistin expression by these cells is enhanced by treatment with several pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1., TNF-., IFN-., or IL-6 . In addition, Resistin has been shown to activate endothelial cells in vitro, leading to the production of adhesion molecules, Endothelin-1, and chemokines . |
| Gene Symbol | RETN |
| Standard Curve |
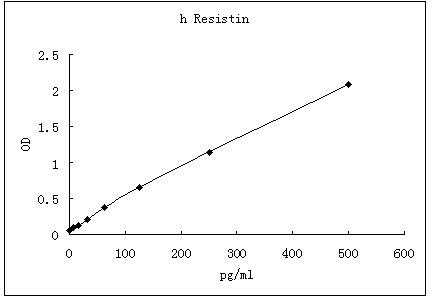
Representative standard curve for Resistin ELISA. Resistin was diluted in serial two-fold steps in Sample Diluent.
|
Documents
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China