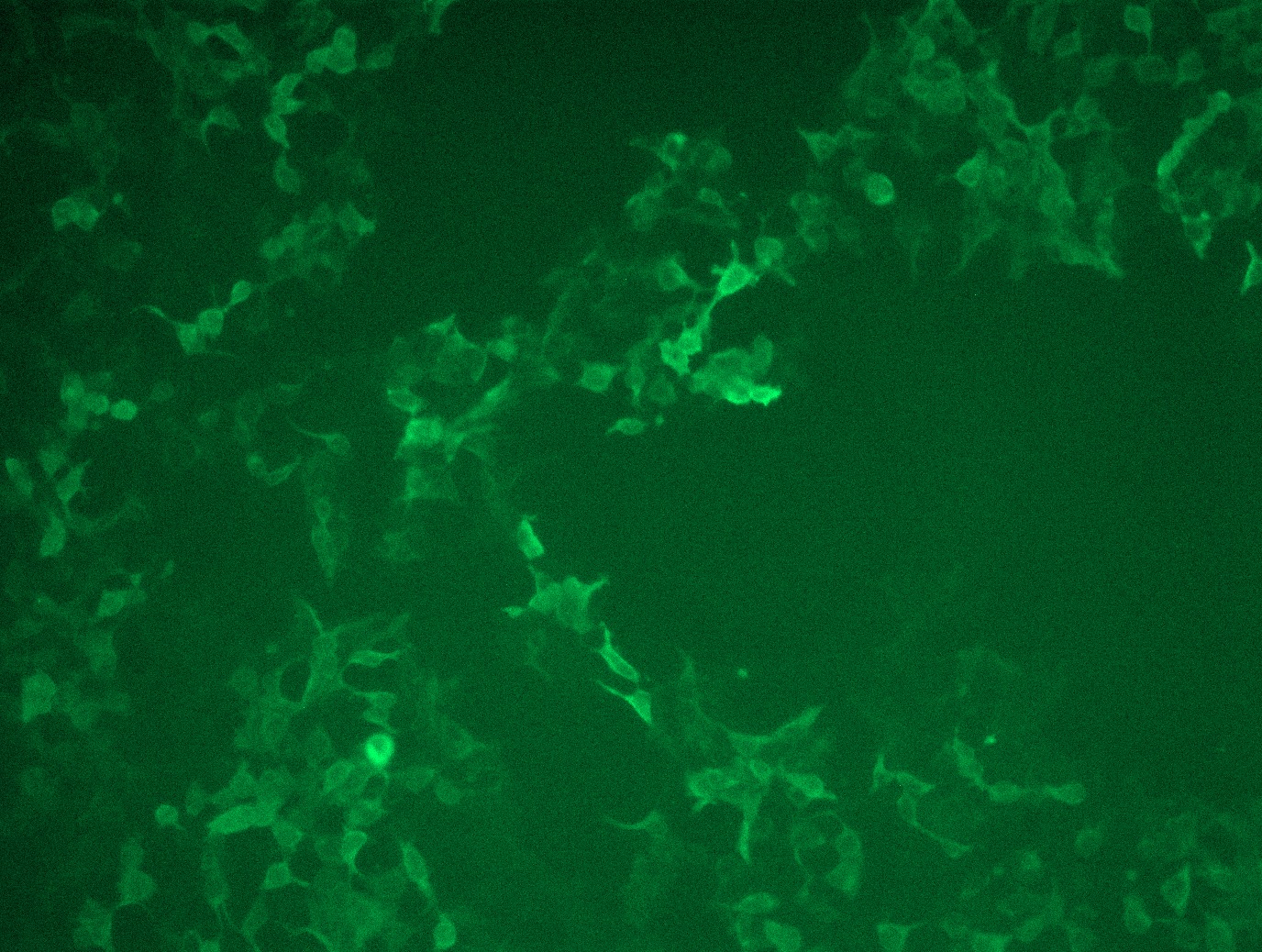
DC SIGN (CD209) (NM_021155) Human Tagged ORF Clone Lentiviral Particle
CAT#: RC220486L3V
- LentiORF®
-

Lenti ORF particles, CD209 (Myc-DDK tagged) - Human CD209 molecule (CD209), transcript variant 1, 200ul, >10^7 TU/mL
Frequently bought together (3)
Other products for "CD209"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Type | Human Tagged ORF Clone Lentiviral Particle |
| Tag | Myc-DDK |
| Symbol | CD209 |
| Synonyms | CDSIGN; CLEC4L; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1; hDC-SIGN |
| Mammalian Cell Selection | Puromycin |
| Vector | pLenti-C-Myc-DDK-P2A-Puro |
| ACCN | NM_021155 |
| ORF Size | 1212 bp |
| Sequence Data |
The ORF insert of this clone is exactly the same as(RC220486).
|
| OTI Disclaimer | The molecular sequence of this clone aligns with the gene accession number as a point of reference only. However, individual transcript sequences of the same gene can differ through naturally occurring variations (e.g. polymorphisms), each with its own valid existence. This clone is substantially in agreement with the reference, but a complete review of all prevailing variants is recommended prior to use. More info |
| OTI Annotation | This clone was engineered to express the complete ORF with an expression tag. Expression varies depending on the nature of the gene. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_021155.2 |
| RefSeq Size | 4266 bp |
| RefSeq ORF | 1215 bp |
| Locus ID | 30835 |
| UniProt ID | Q9NNX6 |
| Cytogenetics | 19p13.2 |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| MW | 45.6 kDa |
| Gene Summary | This gene encodes a C-type lectin that functions in cell adhesion and pathogen recognition. This receptor recognizes a wide range of evolutionarily divergent pathogens with a large impact on public health, including leprosy and tuberculosis mycobacteria, the Ebola, hepatitis C, HIV-1 and Dengue viruses, and the SARS-CoV acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. The protein is organized into four distinct domains: a C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain, a flexible tandem-repeat neck domain, a transmembrane region and an N-terminal cytoplasmic domain involved in internalization. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene, CLEC4M (Gene ID: 10332), also known as L-SIGN. The two genes differ in viral recognition and expression patterns, with this gene showing high expression on the surface of dendritic cells. Polymorphisms in the neck region are associated with protection from HIV-1 infection, while single nucleotide polymorphisms in the promoter of this gene are associated with differing resistance and susceptibility to and severity of infectious disease, including rs4804803, which is associated with SARS severity. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China