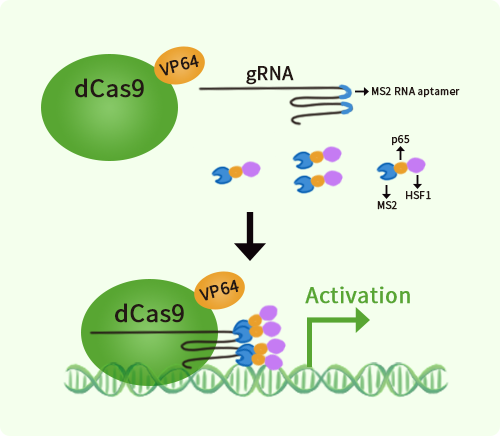
Human CRYGD activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA101002
CRYGD CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human crystallin gamma D
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3gRNAs, 1 scramble ctrl and 1 enhancer vector |
| Symbol | CRYGD |
| Locus ID | 1421 |
| Kit Components | GA101002G1, CRYGD gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA101002G2, CRYGD gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA101002G3, CRYGD gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_006891 |
| Synonyms | CACA; CCA3; CCP; cry-g-D; CRYG4; CTRCT4; PCC |
| Summary | 'Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Gamma-crystallins are a homogeneous group of highly symmetrical, monomeric proteins typically lacking connecting peptides and terminal extensions. They are differentially regulated after early development. Four gamma-crystallin genes (gamma-A through gamma-D) and three pseudogenes (gamma-E, gamma-F, gamma-G) are tandemly organized in a genomic segment as a gene cluster. Whether due to aging or mutations in specific genes, gamma-crystallins have been involved in cataract formation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN422889 | CRYGD - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China