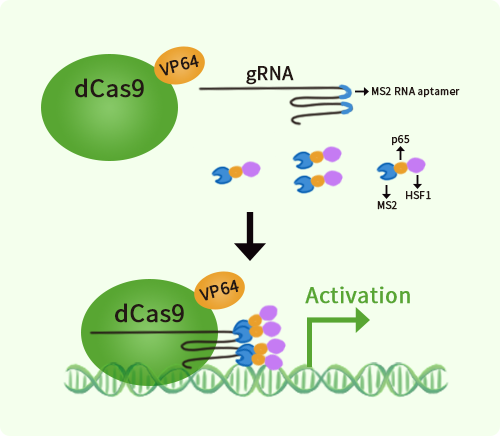
Human PRKAR2B activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA103767
PRKAR2B CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human protein kinase cAMP-dependent type II regulatory subunit beta
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3gRNAs, 1 scramble ctrl and 1 enhancer vector |
| Symbol | PRKAR2B |
| Locus ID | 5577 |
| Kit Components | GA103767G1, PRKAR2B gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA103767G2, PRKAR2B gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA103767G3, PRKAR2B gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_002736 |
| Synonyms | PRKAR2; RII-BETA |
| Summary | 'cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This subunit can be phosphorylated by the activated catalytic subunit. This subunit has been shown to interact with and suppress the transcriptional activity of the cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) in activated T cells. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this subunit may play an important role in regulating energy balance and adiposity. The studies also suggest that this subunit may mediate the gene induction and cataleptic behavior induced by haloperidol. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN409900 | PRKAR2B - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China