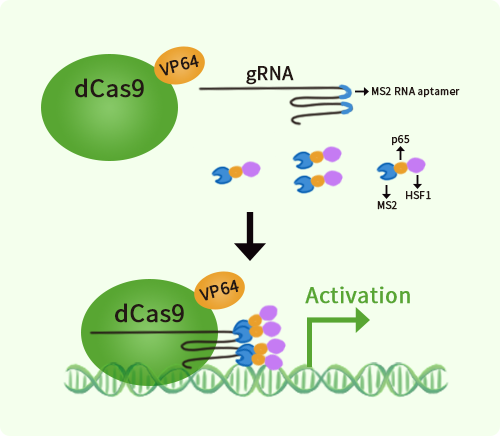
Human DC SIGN (CD209) activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA109395
CD209 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human CD209 molecule
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3gRNAs, 1 scramble ctrl and 1 enhancer vector |
| Symbol | CD209 |
| Locus ID | 30835 |
| Kit Components | GA109395G1, CD209 gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-CRISPRa GA109395G2, CD209 gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-CRISPRa GA109395G3, CD209 gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100058 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001144893, NM_001144894, NM_001144895, NM_001144896, NM_001144897, NM_001144899, NM_021155, NR_026692 |
| Synonyms | CDSIGN; CLEC4L; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN420486 | CD209 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China