Protein Kinase A regulatory subunit I alpha (PRKAR1A) Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN403828
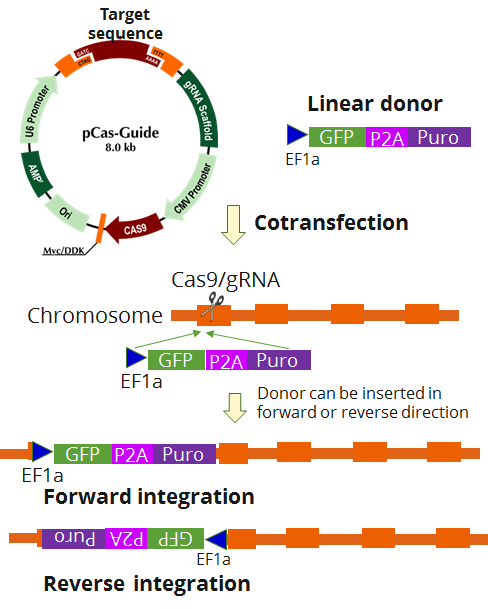
PRKAR1A - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN403828 is the updated version of KN203828.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "Protein Kinase A regulatory subunit I alpha"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | Protein Kinase A regulatory subunit I alpha |
| Locus ID | 5573 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001276289, NM_001276290, NM_001278433, NM_002734, NM_212471, NM_212472, NM_001369389, NM_001369390 |
| Synonyms | ACRDYS1; ADOHR; CAR; CNC; CNC1; PKR1; PPNAD1; PRKAR1; TSE1 |
| Summary | 'cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. This gene encodes one of the regulatory subunits. This protein was found to be a tissue-specific extinguisher that down-regulates the expression of seven liver genes in hepatoma x fibroblast hybrids. Mutations in this gene cause Carney complex (CNC). This gene can fuse to the RET protooncogene by gene rearrangement and form the thyroid tumor-specific chimeric oncogene known as PTC2. A nonconventional nuclear localization sequence (NLS) has been found for this protein which suggests a role in DNA replication via the protein serving as a nuclear transport protein for the second subunit of the Replication Factor C (RFC40). Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA103764 | PRKAR1A CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human protein kinase cAMP-dependent type I regulatory subunit alpha |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China