SLC19A3 Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN406409
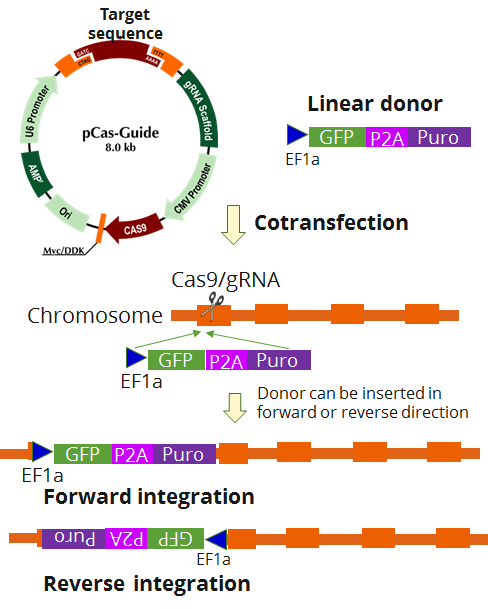
SLC19A3 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN406409 is the updated version of KN206409.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "SLC19A3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | SLC19A3 |
| Locus ID | 80704 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_025243 |
| Synonyms | BBGD; THMD2; THTR2 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a ubiquitously expressed transmembrane thiamine transporter that lacks folate transport activity. Mutations in this gene cause biotin-responsive basal ganglia disease (BBGD); a recessive disorder manifested in childhood that progresses to chronic encephalopathy, dystonia, quadriparesis, and death if untreated. Patients with BBGD have bilateral necrosis in the head of the caudate nucleus and in the putamen. Administration of high doses of biotin in the early progression of the disorder eliminates pathological symptoms while delayed treatment results in residual paraparesis, mild cognitive disability, or dystonia. Administration of thiamine is ineffective in the treatment of this disorder. Experiments have failed to show that this protein can transport biotin. Mutations in this gene also cause a Wernicke's-like encephalopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA112948 | SLC19A3 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human solute carrier family 19 member 3 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China