AVPR V2 (AVPR2) Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN410914
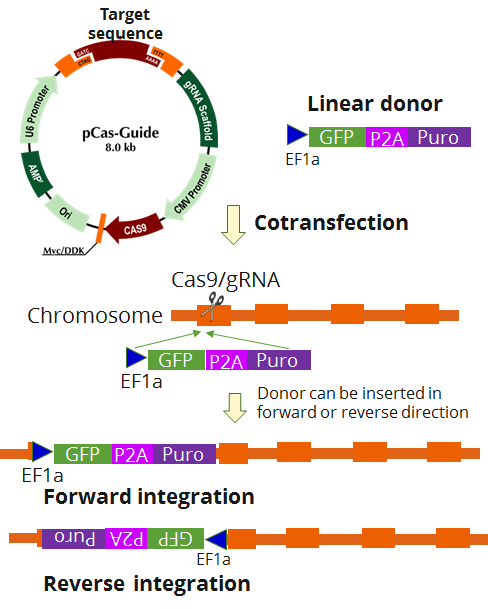
AVPR2 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN410914 is the updated version of KN210914.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "AVPR V2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | AVPR V2 |
| Locus ID | 554 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000054, NM_001146151, NR_027419 |
| Synonyms | ADHR; DI1; DIR; DIR3; NDI; V2R |
| Summary | 'This gene encodes the vasopressin receptor, type 2, also known as the V2 receptor, which belongs to the seven-transmembrane-domain G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, and couples to Gs thus stimulating adenylate cyclase. The subfamily that includes the V2 receptor, the V1a and V1b vasopressin receptors, the oxytocin receptor, and isotocin and mesotocin receptors in non-mammals, is well conserved, though several members signal via other G proteins. All bind similar cyclic nonapeptide hormones. The V2 receptor is expressed in the kidney tubule, predominantly in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts, where its primary property is to respond to the pituitary hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP) by stimulating mechanisms that concentrate the urine and maintain water homeostasis in the organism. When the function of this gene is lost, the disease Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI) results. The V2 receptor is also expressed outside the kidney although its tissue localization is uncertain. When these 'extrarenal receptors' are stimulated by infusion of a V2 selective agonist (dDAVP), a variety of clotting factors are released into the bloodstream. The physiologic importance of this property is not known - its absence does not appear to be detrimental in NDI patients. The gene expression has also been described in fetal lung tissue and lung cancer associated with alternative splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA100384 | AVPR2 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human arginine vasopressin receptor 2 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China