ORP150 (HYOU1) Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN414178
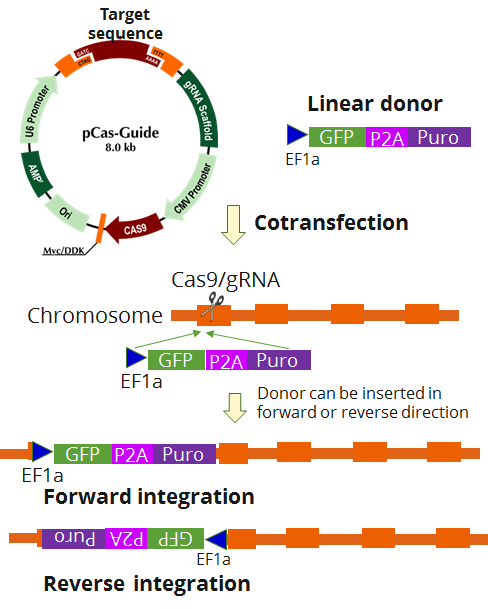
HYOU1 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN414178 is the updated version of KN214178.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "HYOU1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | HYOU1 |
| Locus ID | 10525 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001130991, NM_006389 |
| Synonyms | GRP-170; Grp170; HSP12A; ORP-150; ORP150 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the heat shock protein 70 family. This gene uses alternative transcription start sites. A cis-acting segment found in the 5' UTR is involved in stress-dependent induction, resulting in the accumulation of this protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) under hypoxic conditions. The protein encoded by this gene is thought to play an important role in protein folding and secretion in the ER. Since suppression of the protein is associated with accelerated apoptosis, it is also suggested to have an important cytoprotective role in hypoxia-induced cellular perturbation. This protein has been shown to be up-regulated in tumors, especially in breast tumors, and thus it is associated with tumor invasiveness. This gene also has an alternative translation initiation site, resulting in a protein that lacks the N-terminal signal peptide. This signal peptide-lacking protein, which is only 3 amino acids shorter than the mature protein in the ER, is thought to have a housekeeping function in the cytosol. In rat, this protein localizes to both the ER by a carboxy-terminal peptide sequence and to mitochondria by an amino-terminal targeting signal. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA107191 | HYOU1 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human hypoxia up-regulated 1 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China