Azin1 Mouse Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN501902
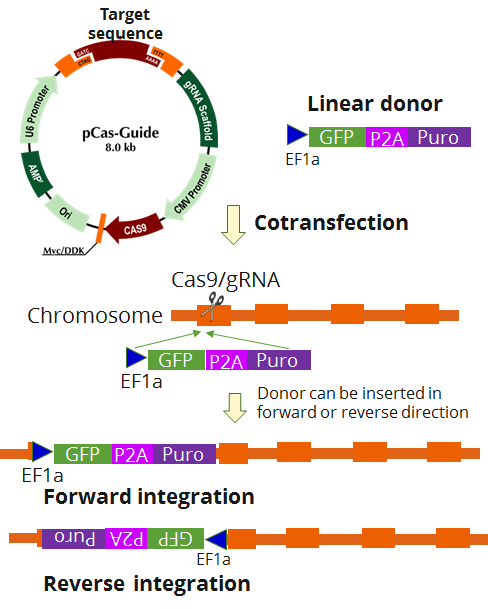
Azin1 - KN2.0, Mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN501902 is the updated version of KN301902.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "Azin1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | Azin1 |
| Locus ID | 54375 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_001102458, NM_001301688, NM_018745, NR_125913 |
| Synonyms | 1700085L02Rik; AZI; Oazi; Oazin |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the antizyme inhibitor family, which plays a role in cell growth and proliferation by maintaining polyamine homeostasis within the cell. Antizyme inhibitors are homologs of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC, the key enzyme in polyamine biosynthesis) that have lost the ability to decarboxylase ornithine; however, retain the ability to bind to antizymes. Antizymes negatively regulate intracellular polyamine levels by binding to ODC and targeting it for degradation, as well as by inhibiting polyamine uptake. Antizyme inhibitors function as positive regulators of polyamine levels by sequestering antizymes and neutralizing their effect. This gene encodes antizyme inhibitor 1, the first member of this gene family that is ubiquitously expressed, and is localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Overexpression of antizyme inhibitor 1 gene has been associated with increased proliferation, cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Gene knockout studies showed that homozygous mutant mice lacking functional antizyme inhibitor 1 gene died at birth with abnormal liver morphology. RNA editing of this gene, predominantly in the liver tissue, has been linked to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA205685 | Azin1 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of mouse antizyme inhibitor 1 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China