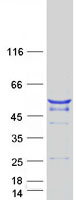
alpha Tubulin (TUBA1A) (NM_006009) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH308669
TUBA1A MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_006000)
Other products for "TUBA1A"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC208669 |
| Predicted MW | 50.1 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC208669 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MRECISIHVGQAGVQIGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFNTFFSETGAGKHVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRTGTYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDLVLDRIRKLADQCTGLQGFLVFHS FGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIY DICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLIGQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEK AYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIATIKTKRTIQFVDWCPTG FKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSE AREDMAALEKDYEEVGVDSVEGEGEEEGEEY TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | 50 ug/ml as determined by BCA |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 100 mM glycine, 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.3. Store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Stable for 3 months from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_006000 |
| RefSeq Size | 1930 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1353 |
| Synonyms | B-ALPHA-1; LIS3; TUBA3 |
| Locus ID | 7846 |
| UniProt ID | Q71U36 |
| Cytogenetics | 12q13.12 |
| Summary | Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species. This gene encodes alpha tubulin and is highly similar to the mouse and rat Tuba1 genes. Northern blot studies have shown that the gene expression is predominantly found in morphologically differentiated neurologic cells. This gene is one of three alpha-tubulin genes in a cluster on chromosome 12q. Mutations in this gene cause lissencephaly type 3 (LIS3) - a neurological condition characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, and early-onset epilepsy caused by defective neuronal migration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Gap junction, Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China