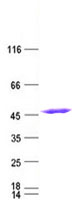
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH1) Mutant (NM_005896) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP710051
Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) and mutant(R132S) heterodimer, with C-terminal polyhistidine and DDK tags, expressed in sf9 cells
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | Sf9 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | Two DNA sequences from TrueORF clone, RC210582 and RC400099, respectively encoding human full-length IDH1 and Mutant IDH1(R132S) |
| Tag | C-DDK |
| Predicted MW | 47 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 50mM Tris-HCl pH8.0, 150mM NaCl, 10%glycerol |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_005887 |
| Locus ID | 3417 |
| Cytogenetics | 2q34 |
| Refseq Size | 2339 |
| Refseq ORF | 1245 |
| Synonyms | HEL-216; HEL-S-26; IDCD; IDH; IDP; IDPC; PICD |
| Summary | 'Isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which utilizes NAD(+) as the electron acceptor and the other NADP(+). Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. Each NADP(+)-dependent isozyme is a homodimer. The protein encoded by this gene is the NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase found in the cytoplasm and peroxisomes. It contains the PTS-1 peroxisomal targeting signal sequence. The presence of this enzyme in peroxisomes suggests roles in the regeneration of NADPH for intraperoxisomal reductions, such as the conversion of 2, 4-dienoyl-CoAs to 3-enoyl-CoAs, as well as in peroxisomal reactions that consume 2-oxoglutarate, namely the alpha-hydroxylation of phytanic acid. The cytoplasmic enzyme serves a significant role in cytoplasmic NADPH production. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]' |
| Protein Pathways | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle), Glutathione metabolism, Metabolic pathways |
Documents
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC401782 | IDH1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY401782 | Transient overexpression lysate of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) |
USD 436.00 |
|
| PH310582 | IDH1 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_005887) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| TP310582 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) |
USD 823.00 |
|
| TP700038 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1 mutant R132H),with C-terminal Myc-DDK tag, expressed in HEK293 cells |
USD 748.00 |
|
| TP700039 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1 mutant R132C),with C-terminal Myc-DDK tag, expressed in HEK293 cells |
USD 748.00 |
|
| TP700040 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1 mutant R132L),with C-terminal Myc-DDK tag, expressed in HEK293 cells |
USD 748.00 |
|
| TP700041 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1 mutant R132S),with C-terminal Myc-DDK tag, expressed in HEK293 cells |
USD 748.00 |
|
| TP700042 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1 mutant R132G),with C-terminal Myc-DDK tag, expressed in HEK293 cells |
USD 748.00 |
|
| TP710042 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1), with C-terminal polyhistidine tag, expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710043 | Recombinant protein of mutant(R132H) of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1),with C-terminal DDK tag,expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710044 | Recombinant protein of mutant(R132C) of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1),with C-terminal DDK tag,expressed in sf9 cells |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710045 | Recombinant protein of mutant(R132L) of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1),with C-terminal DDK tag,expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710046 | Recombinant protein of mutant(R132S) of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1),with C-terminal DDK tag,expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710047 | Recombinant protein of mutant(R132G) of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1),with C-terminal DDK tag,expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710048 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) and mutant(R132H) heterodimer, with C-terminal polyhistidine and DDK tags, expressed in sf9 cells. |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710049 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) and mutant(R132C) heterodimer, with C-terminal polyhistidine and DDK tags, expressed in sf9 cells |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710050 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) and mutant(R132L) heterodimer, with C-terminal polyhistidine and DDK tags, expressed in sf9 cells |
USD 425.00 |
|
| TP710052 | Recombinant protein of human isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) and mutant(R132G) heterodimer, with C-terminal polyhistidine and DDK tags, expressed in sf9 cells |
USD 425.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China