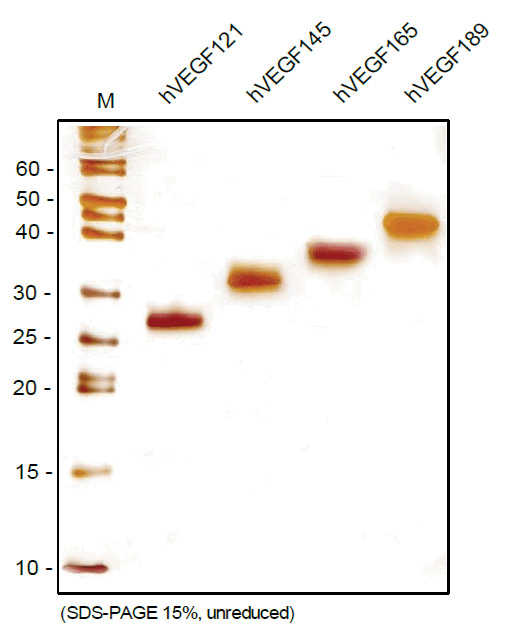
VEGF-A (Isoform 145) Human Protein
Other products for "VEGFA"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
APMAEGGGQNHHEVVKFMDVYQRSYCHPIETLVDIFQEYPDEIEYIFKPSCVPLMRCGGCCNDEGLECVPTEESNITMQIMRIKPHQGQHIGEMSFLQHNKCECRPKKDRARQEKKSVRGKGKGQKRKRKKSRYKSWSVCDKPRR
|
| Predicted MW | 34 kDa |
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE and visualised by silver stain |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Lyophilized puirified protein Buffer System: 50 mM Acetic Acid Preservative: None Stabilizer: None |
| Bioactivity | Biological: The ED50 for stimulation of 3H-thymidine incorporation and cell proliferation by human umbilical vein endothelial cells for VEGF145 has been determined to be in the range of 10 ng/ml. |
| Endotoxin | < 0.1 ng per µg of VEGF145 |
| Reconstitution | Restore in water to a concentration not lower than 50 μg/ml. For long term storage we recommend to add at least 0.1% Human or Bovine Serum Albumin. |
| Preparation | Lyophilized puirified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant Human VEGF145. Result by N-terminal sequencing: APMAEGG |
| Note | Centrifuge vials before opening! |
| Storage | Store lyophilized at 2-8°C for 6 months or at -20°C long term. After reconstitution store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C long term. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001020537 |
| Locus ID | 7422 |
| UniProt ID | P15692 |
| Cytogenetics | 6p21.1 |
| Synonyms | MVCD1; VEGF; VPF |
| Summary | 'This gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It encodes a heparin-binding protein, which exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. This growth factor induces proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, and is essential for both physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Disruption of this gene in mice resulted in abnormal embryonic blood vessel formation. This gene is upregulated in many known tumors and its expression is correlated with tumor stage and progression. Elevated levels of this protein are found in patients with POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) and atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. There is also evidence for alternative translation initiation from upstream non-AUG (CUG) codons resulting in additional isoforms. A recent study showed that a C-terminally extended isoform is produced by use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon via a stop codon readthrough mechanism, and that this isoform is antiangiogenic. Expression of some isoforms derived from the AUG start codon is regulated by a small upstream open reading frame, which is located within an internal ribosome entry site. The levels of VEGF are increased during infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), thus promoting inflammation by facilitating recruitment of inflammatory cells, and by increasing the level of angiopoietin II (Ang II), one of two products of the SARS-CoV-2 binding target, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In turn, Ang II facilitates the elevation of VEGF, thus forming a vicious cycle in the release of inflammatory cytokines. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2020]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Secreted Protein |
| Protein Pathways | Bladder cancer, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Focal adhesion, mTOR signaling pathway, Pancreatic cancer, Pathways in cancer, Renal cell carcinoma, VEGF signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China