PPM1D (98-375, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "PPM1D"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MVAFFAVCDG HGGREAAQFA REHFWGFIKK QKGFTSSEPA KVCAAIRKGF LACHLAMWKK LAEWPKTMTG LPSTSGTTAS VVIIRGMKMY VAHVGDSGVV LGIQDDPKDD FVRAVEVTQD HKPELPKERE RIEGLGGSVM NKSGVNRVVW KRPRLTHNGP VRRSTVIDQI PFLAVARALG DLWSYDFFSG EFVVSPEPDT SVHTLDPQKH KYIILGSDGL WNMIPPQDAI SMCQDQEEKK YLMGEHGQSC AKMLVNRALG RWRQRMLRAD NTSAIVICI
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 33.2 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
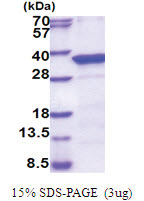
| Purity | >90% by SDS - PAGE |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: Liquid, In 20mM Tris-HCl (pH8.0) containing 10% glycerol. |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human PPM1D, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_003611 |
| Locus ID | 8493 |
| UniProt ID | O15297, A0A0S2Z4M2 |
| Cytogenetics | 17q23.2 |
| Synonyms | IDDGIP; PP2C-DELTA; WIP1 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the PP2C family of Ser/Thr protein phosphatases. PP2C family members are known to be negative regulators of cell stress response pathways. The expression of this gene is induced in a p53-dependent manner in response to various environmental stresses. While being induced by tumor suppressor protein TP53/p53, this phosphatase negatively regulates the activity of p38 MAP kinase, MAPK/p38, through which it reduces the phosphorylation of p53, and in turn suppresses p53-mediated transcription and apoptosis. This phosphatase thus mediates a feedback regulation of p38-p53 signaling that contributes to growth inhibition and the suppression of stress induced apoptosis. This gene is located in a chromosomal region known to be amplified in breast cancer. The amplification of this gene has been detected in both breast cancer cell line and primary breast tumors, which suggests a role of this gene in cancer development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Phosphatase |
| Protein Pathways | p53 signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China