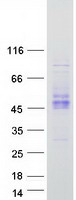
KIR2DS2 (NM_012312) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP311725
Recombinant protein of human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, two domains, short cytoplasmic tail, 2 (KIR2DS2)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC211725. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 31.5 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_036444 |
| Locus ID | 100132285 |
| UniProt ID | P43631, K7R1S5 |
| Cytogenetics | 19q13.4 |
| Refseq Size | 1573 |
| Refseq ORF | 912 |
| Synonyms | 183ActI; CD158b; CD158J; cl-49; KIR-2DS2; NKAT-5; NKAT5 |
| Summary | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. This gene represents a haplotype-specific family member that encodes a protein with a short cytoplasmic tail. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC415836 | KIR2DS2 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY415836 | Transient overexpression lysate of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, two domains, short cytoplasmic tail, 2 (KIR2DS2) |
USD 396.00 |
|
| PH311725 | KIR2DS2 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_036444) |
USD 2,055.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China