LIM Kinase 1 (LIMK1) (NM_002314) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP318058
Recombinant protein of human LIM domain kinase 1 (LIMK1)
Other products for "LIMK1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC218058. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
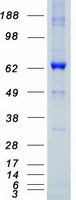
| Predicted MW | 72.4 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_002305 |
| Locus ID | 3984 |
| UniProt ID | P53667 |
| Cytogenetics | 7q11.23 |
| Refseq Size | 3332 |
| Refseq ORF | 1941 |
| Synonyms | LIMK; LIMK-1 |
| Summary | 'There are approximately 40 known eukaryotic LIM proteins, so named for the LIM domains they contain. LIM domains are highly conserved cysteine-rich structures containing 2 zinc fingers. Although zinc fingers usually function by binding to DNA or RNA, the LIM motif probably mediates protein-protein interactions. LIM kinase-1 and LIM kinase-2 belong to a small subfamily with a unique combination of 2 N-terminal LIM motifs and a C-terminal protein kinase domain. LIMK1 is a serine/threonine kinase that regulates actin polymerization via phosphorylation and inactivation of the actin binding factor cofilin. This protein is ubiquitously expressed during development and plays a role in many cellular processes associated with cytoskeletal structure. This protein also stimulates axon growth and may play a role in brain development. LIMK1 hemizygosity is implicated in the impaired visuospatial constructive cognition of Williams syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Axon guidance, Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China