GPR149 (NM_001038705) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP323772
Recombinant protein of human G protein-coupled receptor 149 (GPR149)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC223772. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 80.8 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
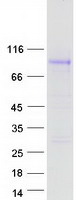
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001033794 |
| Locus ID | 344758 |
| UniProt ID | Q86SP6, Q2MKA6 |
| Cytogenetics | 3q25.2 |
| Refseq Size | 2323 |
| Refseq ORF | 2193 |
| Synonyms | IEDA; PGR10; R35 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) class A family member. Although categorized as a class A GPCR, the encoded protein lacks the first two charged amino acids of the highly conserved Asp-Arg-Tyr (DRY) motif found in the third transmembrane helix of class A receptors which is important for efficient G protein-coupled signal transduction. Mice with a knockout of the orthologous gene are viable and have normal maturation of the ovarian follicle, but show enhanced fertility and ovulation. All GPCRs have a common structural architecture consisting of seven transmembrane alpha-helices interconnected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops. A general feature of GPCR signaling is agonist-induced conformational changes in the receptor, leading to activation of the heterotrimeric G proteins, which consist of the guanine nucleotide-binding G-alpha subunit and the dimeric G-beta-gamma subunits. The activated G proteins then bind to and activate numerous downstream effector proteins, which generate second messengers that mediate a broad range of cellular and physiological processes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, GPCR, Transmembrane |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC422009 | GPR149 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 187.00 |
|
| LY422009 | Transient overexpression lysate of G protein-coupled receptor 149 (GPR149) |
USD 605.00 |
|
| PH323772 | GPR149 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_001033794) |
USD 2,055.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China