DNMT1 (NM_001130823) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP326414
Recombinant protein of human DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), transcript variant 1
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC226414. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 184.6 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
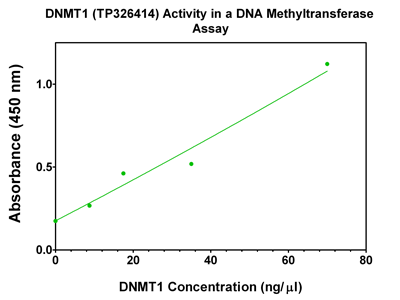
| Bioactivity | DNMT1 activity verified in a biochemical assay: DNMT1 (DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1) (TP326414) is a key methyltransferase that is responsible for maintaining methylation patterns established in development. DNMT1 preferentially methylates hemi-methylated CpG di-nucleotides and associates with DNA replication sites in S phase maintaining the methylation pattern in the newly synthesized strand. Varying concentrations of DNMT1 were added to a microplate containing a bound methyltransferase substrate. After incubation, the resulting methylated DNA residues were detected immunologically and a colorimetric signal was generated and measured. |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001124295 |
| Locus ID | 1786 |
| UniProt ID | P26358, I6L9H2 |
| Cytogenetics | 19p13.2 |
| Refseq ORF | 4896 |
| Synonyms | ADCADN; AIM; CXXC9; DNMT; HSN1E; m.HsaI; MCMT |
| Summary | 'This gene encodes an enzyme that transfers methyl groups to cytosine nucleotides of genomic DNA. This protein is the major enzyme responsible for maintaining methylation patterns following DNA replication and shows a preference for hemi-methylated DNA. Methylation of DNA is an important component of mammalian epigenetic gene regulation. Aberrant methylation patterns are found in human tumors and associated with developmental abnormalities. Variation in this gene has been associated with cerebellar ataxia, deafness, and narcolepsy, and neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type IE. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Cysteine and methionine metabolism, Metabolic pathways |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC427274 | DNMT1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 187.00 |
|
| LY427274 | Transient overexpression lysate of DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), transcript variant 1 |
USD 665.00 |
|
| PH326414 | DNMT1 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_001124295) |
USD 2,055.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China