B4GALT1 (NM_001497) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP761897
Purified recombinant protein of Human UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (B4GALT1), full length, with N-terminal GST and C-terminal His tag, expressed in E. coli, 50ug
Other products for "B4GALT1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding human full-length B4GALT1
|
| Tag | N-GST and C-His |
| Predicted MW | 71.7 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
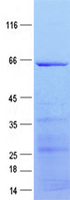
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25mM Tris, pH8.0,150mM NaCl,10% glycerol,1%Sarkosyl |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001488 |
| Locus ID | 2683 |
| UniProt ID | P15291 |
| Cytogenetics | 9p21.1 |
| Refseq Size | 4080 |
| Refseq ORF | 1194 |
| Synonyms | B4GAL-T1; beta4Gal-T1; CDG2D; GGTB2; GT1; GTB |
| Summary | 'This gene is one of seven beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase (beta4GalT) genes. They encode type II membrane-bound glycoproteins that appear to have exclusive specificity for the donor substrate UDP-galactose; all transfer galactose in a beta1,4 linkage to similar acceptor sugars: GlcNAc, Glc, and Xyl. Each beta4GalT has a distinct function in the biosynthesis of different glycoconjugates and saccharide structures. As type II membrane proteins, they have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. This gene is unique among the beta4GalT genes because it encodes an enzyme that participates both in glycoconjugate and lactose biosynthesis. For the first activity, the enzyme adds galactose to N-acetylglucosamine residues that are either monosaccharides or the nonreducing ends of glycoprotein carbohydrate chains. The second activity is restricted to lactating mammary tissues where the enzyme forms a heterodimer with alpha-lactalbumin to catalyze UDP-galactose + D-glucose <=> UDP + lactose. The two enzymatic forms result from alternate transcription initiation sites and post-translational processing. Two transcripts, which differ only at the 5' end, with approximate lengths of 4.1 kb and 3.9 kb encode the same protein. The longer transcript encodes the type II membrane-bound, trans-Golgi resident protein involved in glycoconjugate biosynthesis. The shorter transcript encodes a protein which is cleaved to form the soluble lactose synthase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Galactose metabolism, Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series, Keratan sulfate biosynthesis, Metabolic pathways, N-Glycan biosynthesis |
Documents
| FAQs |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China