PTEN (NM_000314) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP762463
Purified recombinant protein of Human phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), Asn228-End, with N-terminal His tag, expressed in E.coli, 50ug
Other products for "PTEN"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding the region(Asn228-End) of PTEN
|
| Tag | N-His |
| Predicted MW | 20.5 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
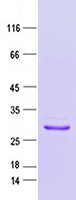
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 50mM Tris, pH8.0, 8M Urea |
| Storage | Store at -80°C after receiving vials. |
| Stability | Stable for at least 1 year from receipt of products under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_000305 |
| Locus ID | 5728 |
| UniProt ID | P60484, F6KD01 |
| Cytogenetics | 10q23.31 |
| Refseq Size | 5572 |
| Refseq ORF | 1209 |
| Synonyms | 10q23del; BZS; CWS1; DEC; GLM2; MHAM; MMAC1; PTEN1; PTENbeta; TEP1 |
| Summary | 'This gene was identified as a tumor suppressor that is mutated in a large number of cancers at high frequency. The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase. It contains a tensin like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. Unlike most of the protein tyrosine phosphatases, this protein preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. It negatively regulates intracellular levels of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in cells and functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating AKT/PKB signaling pathway. The use of a non-canonical (CUG) upstream initiation site produces a longer isoform that initiates translation with a leucine, and is thought to be preferentially associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane. This longer isoform may help regulate energy metabolism in the mitochondria. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 9. Alternative splicing and the use of multiple translation start codons results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2015]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Phosphatase |
| Protein Pathways | Endometrial cancer, Focal adhesion, Glioma, Inositol phosphate metabolism, Melanoma, p53 signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, Phosphatidylinositol signaling system, Prostate cancer, Small cell lung cancer, Tight junction |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China