| Immunogen |
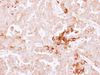
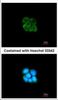
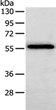
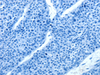
Apha-2 antiplasmin is a single-chain glycoprotein with a molecular weight of about 65,000. The normal concentration in human plasma is 60 μg/ml. Platelets contain significant amounts of the protein, which is released along with platelet factor 4, following thrombin stimulation. It can form 1:1 complexes with circulating plasmin. Alpha-2 antiplasmin is the most important inhibitor of plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis, but also capable of inactivating factor XIIa, kallikrein, factor XIa, thrombin and factor Xa. The importance of the alpha-2 antiplasmin as regulator of the fibrinolytic system was detected by the discovery of a congenital deficiency. Alpha-2 antiplasmin has been isolated from pooled plasma. Freund’s complete adjuvant is used in the first step of the immunization procedure. |






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China