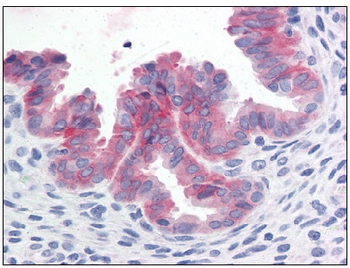
MET (Cytopl. Dom.) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: IST-1]
Other products for "MET"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | IST-1 |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Sections: 1/50. Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 10 µg/ml. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide derived from cytoplasmic domain of Human c-Met protein |
| Specificity | Recognizes c-Met (Cytoplasmic Domain). |
| Formulation | PBS, 7.4 containing 1% BSA and 0.09% Sodium Azide State: Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Storage | Store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase (MET), transcript variant 2 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The c-Met protein is a receptor tyrosine kinase encoded by the c-Met proto-oncogene. c-Met, also known as HGF receptor or SF receptor, is activated by hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or scatter factor (SF), and is composed of alpha and beta subunits linked by disulfide bonds. Dysregulated c-Met expression has been detected at both protein and mRNA levels in a variety of human carcinomas and sarcomas. Up to a 2.5-fold increase in mRNA expression has been reported in colorectal tumor tissues, and upregulation of the c-Met protein in association with increasingly malignant behavior has been described in prostate cancer, cutaneous malignant melanoma, and breast cancer. Recent studies using monoclonal Ms anti-c-Met (clone: 3D4) for immunohistochemistry in lymph node-negative breast carcinoma tissues demonstrated that high levels of c-Met expression are associated with poor patient clinical outcome, as assessed over 20-40 years of follow-up. Further, antibodies against the intracellular but not the extracellular domain of c-Met were prognostic, suggesting that overexpression of the cytoplasmic tail of c-Met may play an important role in breast cancer progression. |
| Synonyms | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor, MET, Scatter factor receptor, HGF/SF receptor, c-Met |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Adherens junction, Axon guidance, Colorectal cancer, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Endocytosis, Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, Focal adhesion, Melanoma, Pathways in cancer, Renal cell carcinoma |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China