Cd14 Rat Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: Sa14-2]
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | Sa14-2 |
| Applications | FC, FN, IF |
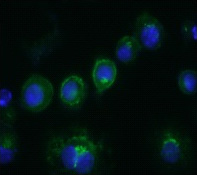
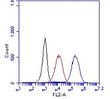
| Recommended Dilution | Flow cytometry (3): The typical starting working dilution is 1:50. Functional assays. Immunoflourescence (4): The typical starting working dilution is 1:50. Positive control: RAW-cells. |
| Reactivities | Mouse |
| Host | Rat |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | CD14 transfectant |
| Specificity | The monoclonal antibody Sa14-2 recognizes the mouse monocyte marker CD14. |
| Formulation | PBS Label: FITC State: Liquid 0.2 µm filtered Ig fraction Stabilizer: 1% bovine serum albumin |
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/ml |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Conjugation | FITC |
| Gene Name | CD14 antigen |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The CD14 receptor is a pattern recognition molecule in the innate immune response against microorganisms and other exogenous and endogenous stress factors. CD14 was characterized as a receptor for LPS. The CD14 gene consists of two exons which code for a single mRNA that is translated into a protein of 375 amino acids. The CD14 protein is composed of eleven leucin-rich repeats, which are also found in TLR and which are important in PAMP binding. In contrast to TLR, however, CD14 lacks a transmembrane domain, and thus cannot initiate intracellular signal transduction by itself. The most important CD14 signaling co-receptor is toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), which activates, among others, the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) inflammatory pathway. The CD14 protein is processed in the endoplasmatic reticulum and expressed as a 55 kDa glycoprotein on the cell surface via a glycosylphosphatidyl (GPI) anchor. Like other GPI-anchored proteins, CD14 accumulates on the cell surface in microdomains known as lipid rafts. CD14 is expressed pre dominantly on the surface of 'myeloid' cells, such as monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils, but at lower levels also on epithelial cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts. |
| Synonyms | CD14 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China