Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: ER505]
CAT#: AM32844PU-S
Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone ER505, Purified
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | ER505 |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
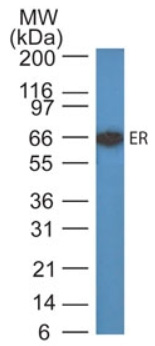
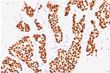
| Recommended Dilution | Western blotting: 0.5-1 µg/ml for 2 hours at RT. Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 0.5-1 µg/ml for 30 minutes at RT. Staining of formalin-fixed tissues requires boiling tissue sections in 10mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at RT for 20 minutes. Positive Control: MCF-7 Cells or Breast Cancers. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein containing amino acids 2-185 of Human Estrogen Receptor alpha. |
| Specificity | This Monoclonal ER505 antibody is specific to ER alpha and shows minimal cross-reaction with other members of the family. ER is an important regulator of growth and differentiation in the mammary gland. Presence of ER in breast tumors indicates an increased likelihood of response to anti-estrogen (e.g. tamoxifen) therapy. This Monoclonal antibody is excellent for staining of Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded breast carcinomas. Cellular Localization: Nucleus. |
| Formulation | 10mM PBS State: Purified State: Liquid purified IgG fraction from Bioreactor Concentrate Stabilizer: 0.05% BSA Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Protein A/G Chromatography |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | ~67 kDa |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The estrogen receptor (ER) is a ~ 67kDa protein, originally described by Jensen and Jacobson, 1962 as a uterine protein which bound 3H-estradiol with high affinity. More than two decades later the cDNA encoding the human estrogen receptor was finally cloned and sequenced. The estrogen receptor gene consists of more than 140kb of genomic DNA divided into 8 exons, being translated into a protein with six functionally discrete domains, labeled A through F. The A/B domain of the estrogen receptor contains a constitutively active transcription activation function called TAF-1. Domain C contains two Cys4 zinc fingers, which form the core of the DNA binding domain; it also contains a weak constitutive dimerization activity. The zinc fingers interact with DNA, and the ER homodimer appears to bind most tightly to the palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence GGATCNNNGATCC. The hinge domain D appears to be the location for binding by heat shock proteins. The estrogen receptor is an important regulator of growth and differentiation in the mammary gland. Estrogens play an important role also in breast cancer development, although tumors often progress towards an autocrine growth. This hormone-independence and the incomplete correlation between ER-status and response to endocrine (tamoxifen) therapy may be explained by the presence of receptor variants with either constitutive transcriptional activity or a dominant negative inhibition of normal ER function. Many investigators have reported on the isolation of cDNAs which encode variant ER sequences. Many of these variants appear to be formed by errors in RNA splicing which result in one or more exons being lost during processing of the ER message. |
| Synonyms | ER alpha, Estradiol receptor, ESR1, ESR, NR3A1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China