MTOR (2440-2457) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | Assay, ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1/4000 - 1/20000. Western Blot: 1/250 - 1/2000. |
| Reactivities | Canine, Human, Mouse, Zebrafish |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 2440-2457 of human mTOR |
| Specificity | Reactivity occurs with both phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of mTOR at S2448 from derived tissues and cells. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 containing 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Immunoaffinity chromatography |
| Storage | Store the antibody at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Database Link | |
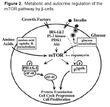
| Background | Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine and threonine protein kinase that regulates numerous cellular functions, in particular, the initiation of protein translation. Rapamycin is a natural product macrolide that induces G1 growth arrest in yeast, Drosophila, and mammalian cells. mTOR has a long list of synonyms including FK506 binding protein12 - rapamycin associated protein 1, FK506 binding protein12 - rapamycin associated protein 2, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 and/or FKBP12-rapamycin associated protein (FRAP). mTOR is one of a family of proteins involved in cell cycle progression, DNA recombination, and DNA damage detection. In rat, mTOR is a 245-kD protein referred to as RAFT1 with significant homology to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein TOR1 and has been shown to associate with the immunophilin FKBP12 in a rapamycin-dependent fashion. The FKBP12-rapamycin complex is known to inhibit progression through the G1 cell cycle stage by interfering with mitogenic signaling pathways involved in G1 progression in several cell types, as well as in yeast. The binding of mTOR to FKBP12-rapamycin correlates with the ability of these ligands to inhibit cell cycle progression. |
| Synonyms | Mammalian target of rapamycin, TOR, FRAP, FRAP2, RAPT1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China
![Western blot using Affinity Purified anti-mTOR antibody shows detection of a band ~245 kDa corresponding to human mTor (arrowhead). Approximately 30 ug of HEK293 cell lysate was separated by 4-8% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose. After blocking, the membrane was probed with the primary antibody diluted to 1:650 for 2h at RT. The membrane was washed and reacted with a 1:10,000 dilution of IRDye (TM)800 conjugated Gt-a-Rabbit IgG [H&L] MX for 45 min at room temperature. IRDye (TM)800 fluorescence image was captured using the Odyssey (R) Infrared Imaging System developed by LI-COR. IRDye is a trademark of LI-COR, Inc. Other detection systems will yield similar results.](https://cdn.origene.com/assets/images/antibody/acris/ap09299pu-n-1-w.jpg)