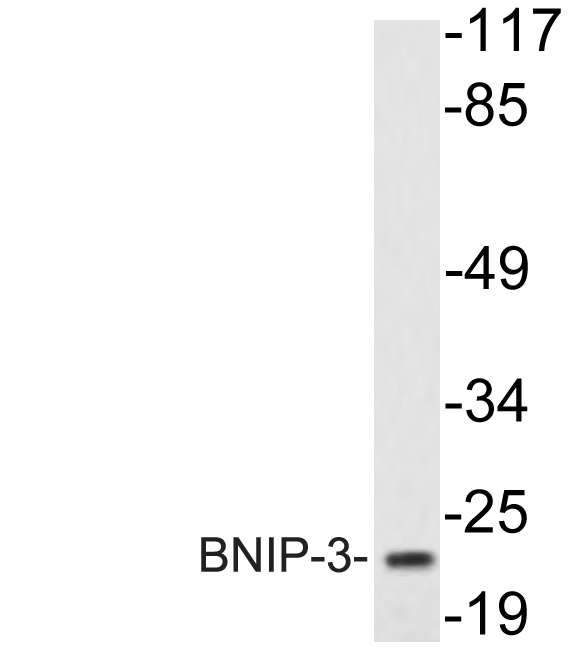
BNIP3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "BNIP3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Western Blot: 1/500-1/1000. Immunohistochemistry on paraffin sections: 1/50 - 1/200. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Specificity | This antibody detects endogenous levels of BNIP-3 protein. (region surrounding Glu96) |
| Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2 State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction Preservative: 0.05% sodium azide |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/ml |
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen; purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE) |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | ~ 22 kDa |
| Gene Name | BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 3 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | BNIP3, formerly NIP3 (nineteen kDa interacting protein-3), is a pro-apoptotic, mitochondrial protein classified in the Bcl 2 family based on limited sequence homology to the Bcl 2 homology 3 (BH3) domain (amino acids 110-118) and C-terminal TM domain. BNIP3 expressed in yeast and mammalian cells interacts with survival promoting proteins Bcl 2, Bcl XL, CED9 and the adenovirus E1B 19K protein. Typically the BH3 domain of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 homologues mediates Bcl 2/Bcl XL heterodimerization and confers pro-apoptotic activity. BNIP3 represents a subfamily of Bcl 2 related proteins, which functions without a typical BH3 domain to regulate apoptosis from both mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial sites by selective Bcl 2/Bcl XL interactions. The N-terminus (residues 1-49) and the C-terminus TM domain of BNIP3 are critical for Bcl 2 heterodimerization, and either region is sufficient for Bcl XL interaction. The TM domain of BNIP3 is critical for homodimerization, pro-apoptotic function, and mitochondrial targeting. BNIP3 contains PEST sequences suggesting that the protein may be susceptible to rapid degradation by proteases. PEST sequences commonly contain high local concentrations of amino acids P, E, S, T, and D flanked by charged amino acids and these are abundantly present in NIP3. Thus, the posttranslational control of BNIP3 expression through rapid protein degradation may constitute a mechanism for regulating the intracellular levels of a potentially lethal protein. |
| Synonyms | BNIP3 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China