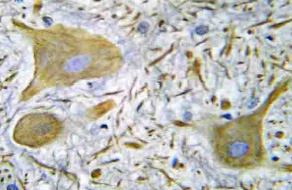
NMDAR1 (GRIN1) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "GRIN1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | Immunohistochemistry on Paraffin Sections: 1/50-1/200. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Specificity | This antibody detects endogenous levels of NMDAR1 protein (region surrounding Ser902). |
| Formulation | PBS, pH~7.2 State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid purified Ig fraction (> 95% by SDS-PAGE) Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/ml |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Predicted Protein Size | ~ 120 kDa |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 1 (GRIN1), transcript variant GluN1-4a |
| Database Link | |
| Background | NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels possesses high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. Plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. It mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Is involved in the cell surface targeting of NMDA receptors. The ion channels activated by glutamate are divided into two classes. Those that are sensitive to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are designated NMDA receptors (NMDAR) while those activated by kainate and a-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalone propionic acid (AMPA) are known as kainate/AMPA receptors (K/AMPAR). NMDA receptors are among the most studied receptors in neuroscience because they are involved in neuronal cell development and plasticity, a cellular correlate for learning. |
| Synonyms | NMDAR1,GRIN1 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Ion Channels: Glutamate Receptors, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Alzheimer's disease, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Calcium signaling pathway, Huntington's disease, Long-term potentiation, Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China