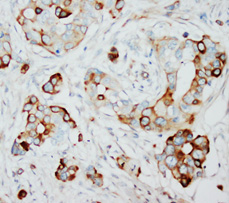
SKP2 (N-term) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "SKP2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IF, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Western blot: At 1μg/ml with the appropriate system to detect SKP2 in cells and tissues. Immunohistochemistry on paraffin sections: At 1-2μg/ml to detect SKP2 in formalin fixed and paraffin embedded tissues. Immunocytochemistry. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the N-terminal of human SKP2 |
| Specificity | This antibody detects SKP2 / FBXL1 (N-term). No cross reactivity with other proteins. |
| Formulation | 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3 State: Aff - Purified State: Lyophilized Ig fraction |
| Reconstitution Method | 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500μg/ml. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified |
| Storage | Store at 2 - 8 °C for up to one month or (in aliquots) at -20 °C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens S-phase kinase-associated protein 2, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (SKP2), transcript variant 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The F box protein Skp2 (S-phase kinase-associated protein 2) is oncogenic, and its frequent amplification and overexpression correlate with the grade of malignancy of certain tumors. Skp2 controls p300-p53 signaling pathways in cancer cells, making it a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. This gene positively regulates the G(1)-S transition by controlling the stability of several G(1) regulators, such as the cell cycle inhibitor p27. This study provides evidence of a role for an F-box protein in oncogenesis and establishes SKP2 as a protooncogene causally involved in the pathogenesis of lymphomas. |
| Synonyms | FBL1; FBXL1; FLB1; MGC1366; p45skp2 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Acute myeloid leukemia, Apoptosis, Cell cycle, Oocyte meiosis, p53 signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation, Small cell lung cancer, Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China