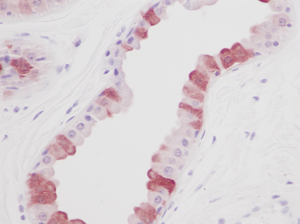
EGF Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "EGF"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ELISA, FN, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | Sandwich ELISA: To detect hEGF by Sandwich ELISA (using 100 µl/well antibody solution) a concentration of at least 0.5-0.2 µg/ml of this antibody is required. This antigen affinity purified antibody, in conjunction with Biotin conjugated anti-Human EGF (PP1002B) as a detection antibody allows the detection of at least 0.2-0.4 ng/well of recombinant hEGF. Western Blot: To detect hEGF by Western Blot analysis this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1-0.2 µg/ml. Used in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents the detection limit for recombinant hEGF is 1.5-3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions. Neutralization: To yield one-half maximal inhibition [ND50] of the biological activity of hEGF (2.0 ng/ml), a concentration of 0.25-0.35 µg/ml of this antibody is required. Immunohistochemistry on Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Sections: 1-0.25 µg/ml overnight at 4°C. An HRP-labeled polymer detection system was used with a non-alcohol soluble AEC chromogen and a proteinase K antiegen retrieval. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Highly pure (>98%) E.coli derived recombinant Human EGF (hEGF). |
| Specificity | Human Epidermal Growth Factor (hEGF) |
| Formulation | PBS, pH 7.2 without preservatives. State: Aff - Purified State: Lyophilized (sterile filtered) purified Ig fraction. |
| Reconstitution Method | Restore in sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography using an immobilized Human EGF matrix |
| Storage | Store the antibody prior to reconstitution at -20°C. Following reconstitution the antibody can be stored at 2-8°C for one month or at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: One year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens epidermal growth factor (EGF), transcript variant 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Epidermal growth factor (EGF) has a profound effect on the differentiation of specific cells in vivo and is a potent mitogenic factor for a variety of cultured cells. The EGF precursor is believed to exist as a membrane bound molecule which is proteolytically cleaved to generate the 53 amino acid peptide hormone that stimulates cells to divide. EGF exerts its actions by binding to the EGFR, a 170 kDa protein. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a key growth factor regulating cell survival. Through its binding to cell surface receptors, EGF activates an extensive network of signal transduction pathways that include activation of the PI3K/AKT, RAS/ERK and JAK/STAT pathways. Because of its key role in driving the proliferation of cells, EGFR is a target of several anti-cancer drugs currently in development. |
| Synonyms | Urogastrone, Epidermal growth factor, URG, HOMG4 |
| Note | Centrifuge vial prior to opening! |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Adult stem cells, Druggable Genome, Embryonic stem cells, ES Cell Differentiation/IPS, Induced pluripotent stem cells, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Bladder cancer, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Endocytosis, Endometrial cancer, ErbB signaling pathway, Focal adhesion, Gap junction, Glioma, MAPK signaling pathway, Melanoma, Non-small cell lung cancer, Pancreatic cancer, Pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China