Leptin (LEP) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ELISA, WB |
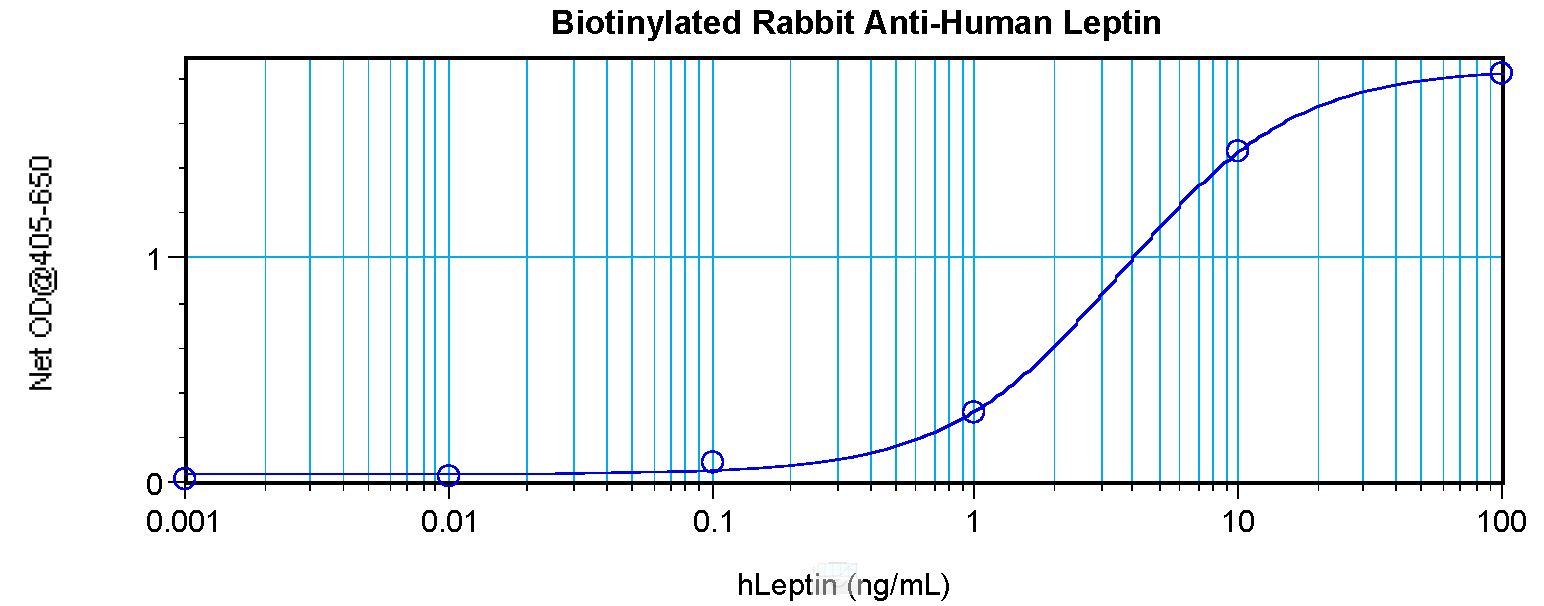
| Recommended Dilution | Direct ELISA: To detect Human Leptin by Direct ELISA (using 100 μl/well antibody solution) a concentration of 0.25-1.0 μg/ml of this antibody is required. This antibody, in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents, allows the detection of at least 0.2-0.4 ng/well of recombinant Human Leptin. Sandwich ELISA: To detect Human Leptin by Sandwich ELISA (using 100 μl/well antibody solution) a concentration of 0.25-1.0 μg/ml of this antibody is required. This biotinylated antibody, in conjunction with Anti-Human Leptin (Cat.-No PP1041P) as a capture antibody, allows the detection of at least 0.2-0.4 ng/well of recombinant hLeptin. Western Blot: To detect Human Leptin by Western Blot analysis this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1-0.2 µg/ml. Used in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents the detection limit for recombinant Human Leptin is 1.5-3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Highly pure (>98%) E.coli derived recombinant Human Leptin (Cat.-No PA094) |
| Specificity | This antibody reacts with Human Leptin. Other species not tested. |
| Formulation | PBS, pH 7.2 without preservatives Label: Biotin State: Lyophilized (sterile filtered) purified Ig fraction. Label: conjugated |
| Reconstitution Method | Restore in sterile PBS containing 0.1% BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. Centrifuge vial prior to opening! |
| Purification | Affinity Chromatography |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| Storage | Prior to reconstitution store at 2-8°C. Following reconstitution store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Leptin plays a critical role in the regulation of body weight by inhibiting food intake and stimulating energy expenditure. Defects in Leptin production cause severe hereditary obesity in rodents and humans. In addition to its effects on body weight, leptin has a variety of other functions, including the regulation of hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, wound healing, and the immune and inflammatory response. The Leptin gene is the human homolog of the gene (ob) mutant in the mouse 'obese' phenotype. Defects in the Leptin gene are the cause of profound obesity and type II diabetes. |
| Synonyms | LEP, OB, OBS, Obesity factor, Obese protein |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China