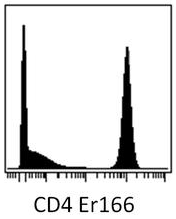
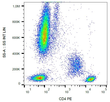
CD4 (N-term) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: MEM-241]
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | MEM-241 |
| Applications | FC |
| Recommended Dilution | Flow Cytometry (1/1500). |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | 2 N-terminal domains of human CD4 fused to human IgG1 Fc |
| Specificity | The antibody recognizes CD4 antigen, a 55 kDa transmebrane glycoprotein expressed on a subset of T lymphocytes (helper T-cells) and also on monocytes, tissue macrophages and granulocytes. |
| Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 15 mM sodium azide, approx. pH 7.4 Label: Biotin State: Liquid purified Ig fraction Label: Conjugated with Biotin-LC-NHS under optimum conditions. The reagent is free of unconjugated biotin. |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/ml |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| Database Link | |
| Background | CD4 is a single chain transmembrane glycoprotein and belongs to immunoglobulin supergene family. In extracellular region there are 4 immunoglobulin-like domains (1 Ig-like V-type and 3 Ig-like C2-type). Transmembrane region forms 25 aa, cytoplasmic tail consists of 38 aa. Domains 1,2 and 4 are stabilized by disulfide bonds. The intracellular domain of CD4 is associated with p56Lck, a Src-like protein tyrosine kinase. It was described that CD4 segregates into specific detergent-resistant T-cell membrane microdomains. Extracellular ligands: MHC class II molecules (binds to CDR2-like region in CD4 domain 1); HIV envelope protein gp120 (binds to CDR2-like region in CD4 domain 1); IL-16 (binds to CD4 domain 3), Human seminal plasma glycoprotein gp17 (binds to CD4 domain 1), L-selectin Intracellular ligands: p56Lck CD4 is a co-receptor involved in immune response (co-receptor activity in binding to MHC class II molecules) and HIV infection (human immunodeficiency virus; CD4 is primary receptor for HIV-1 surface glycoprotein gp120). CD4 regulates T-cell activation, T/B-cell adhesion, T-cell diferentiation, T-cell selection and signal transduction. Defects in antigen presentation (MHC class II) cause dysfunction of CD4+ T-cells and their almost complete absence in patients blood, tissue and organs (SCID immunodeficiency). |
| Synonyms | T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China